It’s impossible to overstate just how important information security is to a company. Your data is what keeps most businesses running. And as data breaches become more common and sophisticated, you need to have a strategy in place for them. Hopefully, your company will never have to respond to a data breach. But it’s nice to have peace of mind knowing you’re prepared in case it does happen.
A thought-through security strategy is not enough, though. You should also be putting policies into place that will help keep your organization safe. Protecting sensitive data should be the number one priority. And it can help maintain trust with your company’s customers and stakeholders.
In this article, you’ll see what a well-designed information security strategy entails. I’ll also go over the phases and steps that are essential in creating a strong plan so that you can make one for your team.
What is information security strategy?
Let’s start with the basics. An information security strategy is a complete plan that protects your company’s data. The last thing you’d want is for someone to get unauthorized access to sensitive information so they could download it, edit it, or even destroy it.
A strong security plan outlines the policies and procedures your IT team will take in the event of a cybersecurity threat. This ensures that everyone is on the same page and can respond as quickly as possible.
An effective infosec strategy takes into account all the unique risks of your company. Every organization’s vulnerabilities are different, along with any legal and regulatory requirements.
Your plan should also take into account the needs of the business. That way, all downtime and interruptions are kept to a minimum. In other words, the most effective information security strategies are risk-aware and aligned with your company’s business.
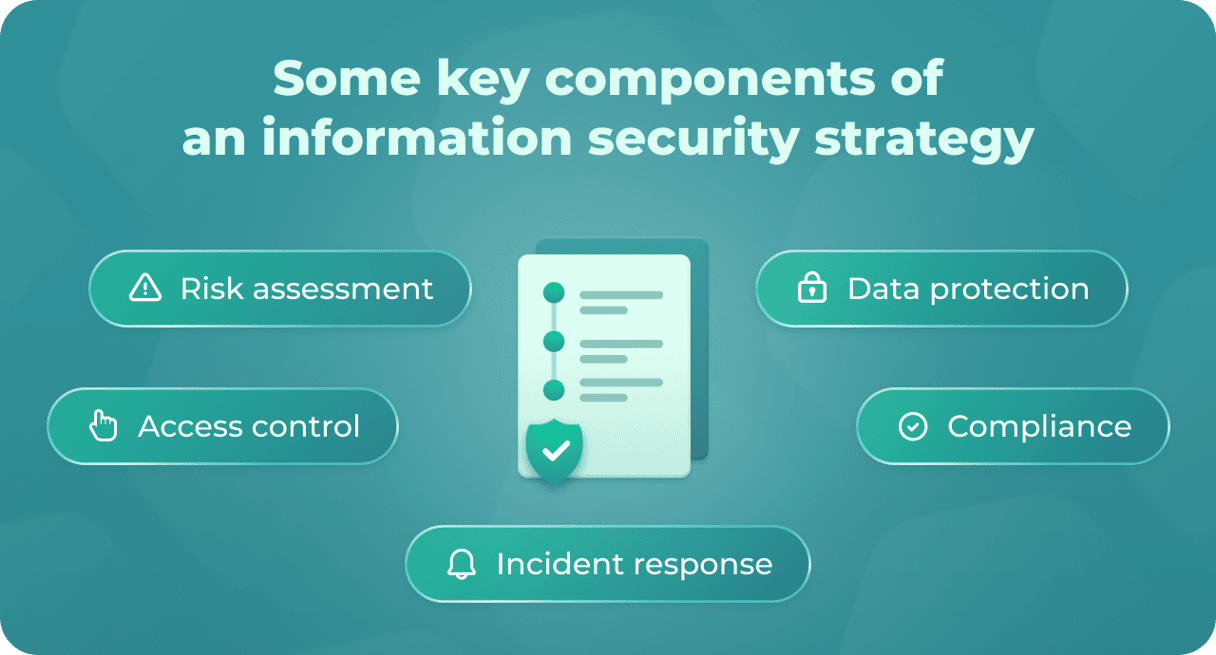
A few key components of a strong information security plan include:
- Risk assessment and management: identifies and assesses the risks to the organization’s information and technology assets as well as implements measures necessary to mitigate those risks.
- Access control: establishes policies and procedures for controlling who has access to sensitive information and data along with the actions they can perform with that information.
- Data protection: implements policies that will protect the sensitive information your company stores. It should take into account measures that are often overlooked, such as encryption, backup, and recovery procedures.
- Incident response and management: establishes the process for responding to and managing security incidents. That way, if a data breach or cyber attack occurs, your team will know how to handle it.
Compliance: ensures that the organization is in compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
Why do I need an information security strategy?
Depending on the industry that your company is in, there might be unique requirements and compliance regulations you need to follow. A well-crafted strategy can help ensure that your organization stays in compliance.
Another key benefit of having a security strategy is that it helps protect your customers’ sensitive information. Whether it’s credit card numbers or social security information, if your business collects it, then it’s your business’ responsibility. The last thing you’d want is to suffer a data breach that causes you to lose all of that private information.
The last thing to consider is the financial angle of an infosec strategy. Most people don’t think about just how costly cyber attacks can be. And I’m not just talking about ransomware costing you a small fortune. Your company might have to think about rebuilding or upgrading the portions of the environment that was breached. That’s even before you take into account any legal fees and fines for not being compliant.
A solid security strategy shows your leadership and your customers that you’re taking the necessary steps to protect company data. You can give everyone just a bit more peace of mind by showing them that your company will be protected from potential threats from cyber criminals.
Phases of information security strategy
Creating an information security strategy is a complex and ongoing process that involves multiple phases. I know it might seem like a lot to get through, but please stick with it. Trust me, the benefits of an information security strategy outweighs what could happen without one.
Phase 1. Assessment
The first phase is to assess your company’s current security situation. How relaxed is your company? Or maybe it’s fairly locked down. Whatever that looks like, putting it down on paper can help you establish the work that still needs to be done.
You’ll probably notice there’s a bit of a domino effect at play in this phase. As you identify what assets need to be protected, then you’ll start to see what potential risks those cause. Then, you’ll be able to figure out what security measures need to be put in place. All while prioritizing what needs to be addressed first.
Phase 2. Planning
The next phase is all about planning. That means it’s time to figure out your company’s security objectives. Whether it’s to ensure confidentiality or just comply with legal regulations, setting a goal to drive towards can help streamline your planning process.
Then, once you have those objectives defined, you’ll also be able to look at risk management and asset control policies. During this stage, it is crucial to keep organization culture in mind so that information security strategy is supported during the next steps, along with determining metrics and benchmarking.
Phase 3. Implementation
When you get to the implementation stage, that’s when you’ll really be putting your plan to the test, rolling out and updating firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other admin controls.
Another important element of the implementation phase is designing incident response play and informing the team about handling security breaches.
Phase 4. Monitoring and maintenance
Moving onto the final phase is how you plan to monitor and maintain this strategy. Ongoing efforts ensure that your infosec strategy stays up to date. That means conducting routine security audits, updating the strategy as needed, and ensuring ongoing compliance as standards change over time.
Steps to develop information security strategies
When it comes to the steps of developing an information security strategy, you’ll probably notice some similarities. But the most important takeaway here is that there is no one right way of doing this.
The phases offer a bit of a broader definition, so it might be helpful to start with those and flesh out your own strategy from there. Either way, take this article as a source of inspiration. Figure out what works for your IT team, and run with that.
1. Assess the organization's current security posture
The first step to creating your strategy is to understand the current state of security. You should wrap up this step knowing what needs to be protected, the current level of risk, and what measures are already in place. Assessing this will help your team determine how much risk they currently face and what you need to do first.
2. Identify legal and regulatory requirements
In addition to your own security requirements, your company might also have to abide by other regulations. Keeping all of those in mind will not just protect the sensitive data your company collects, but it will also protect your company too. Understanding these regulations and knowing they regularly change can save you from a headache if you were to ever be audited.
3. Define the security objectives
The next step of your infused plan is to understand the security goals of your company. What do you want to achieve with this new level of security? Are you trying to lower your chances of a cyber attack? Or do you just want to keep your customer data safe?
While there is no right answer, whatever your answers are will dictate what steps you take next.
4. Develop a risk assessment and management plan
Your IT security is only as strong as its weakest link. If you know where your infrastructure is vulnerable, then you can take steps to strengthen it. Creating a risk assessment plan will help you do just that. By routinely auditing your infrastructure, you’ll be able to catch a weakness before a hacker can exploit it.
5. Establish access control policies and procedures
Access control is arguably one of the most important pieces of your security strategy. Companies should create policies detailing who has access to sensitive data. These files should really only be accessed on a need-to-know basis.
Then, after you’ve established these roles, you’ll need tools to manage them. This can include things like firewalls, admin controls, and other security tools.
6. Protect sensitive information and data
Unfortunately, there’s not a single button that can just make your infrastructure magically secure. It’s something you and your team will have to work at doing. It’s not enough to just put security policies in place. You have to get buy-in from everyone — your IT team and the employees at your company. After all, security policies only work if people are following them.
It’s important to do everything you can to keep it secure. But because you need everyone to follow these rules, you’ve got to put an emphasis on making them easy, too. So, when you’re auditing new systems and applications, keep that in mind. The easier it is for someone not in IT to use, the more secure it’s going to be for your company.
7. Develop an incident response and management plan
Not that anyone wants to deal with a data breach. But it’s important to have a response plan in place before one happens. The incident response and management plan should include procedures for detecting and reporting incidents, conducting investigations, and taking corrective action necessary to prevent future incidents.
8. Ensure ongoing compliance
Organizations must ensure that they are in compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes conducting regular security audits and updating the information security strategy as needed.
Overall, an effective information security strategy helps an organization protect its sensitive information and technology assets, maintain the trust of its customers and stakeholders, and reduce the risk of financial and reputational damage that may derive from security incidents. Developing and implementing such a strategy is an ongoing process, meaning that it can and should be adapted to meet newly determined risks and recently implemented requirements.