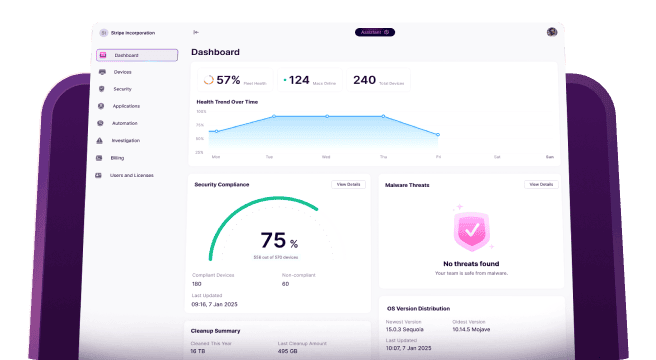
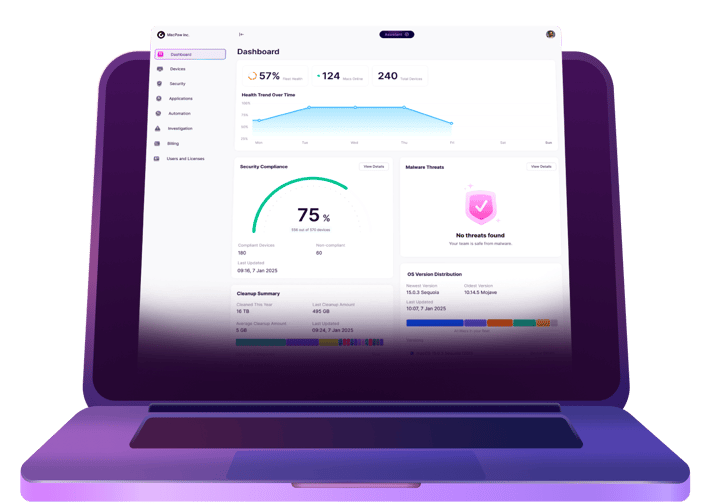
Any IT professional would tell you that their company’s infrastructure is locked down and secure enough. But the reality is that “secure enough” might not actually protect you from a cybersecurity threat. With how often cyber breaches are being talked about in the headlines, your company’s security isn’t something you want to skimp on. Or maybe your company is starting to work with a new partner that requires things to be locked down or hardened even more.
Whatever your reason for wanting to learn more about hardening techniques, you’re in the right place. This article will get into what security hardening is and list out a few of the benefits of doing it.
What is security hardening, and why use security hardening techniques?
First, let’s talk about what is hardening in cyber security. Simply put, it’s the process of mitigating any threats of attacks to your servers and equipment.
A common technique used by IT teams is to reduce the attack surface or cyber vulnerabilities by eliminating equipment and connections not in use. That’s a really long-winded way to say they get rid of the things they’re not using. A prime example of this is terminating network connections that aren’t being used or shutting down old servers.
These dormant connections and pieces of equipment often go unmonitored and are easy targets for hackers.

Best practices for systems hardening
The tricky thing is that cybersecurity hardening can be somewhat subjective depending on what type of business you’re supporting. One of the best things you can do is follow a hardening checklist published by the NIST or CIS Center.
By using one of these checklists as a guide or baseline, you can decide which steps are overkill for your environment or would interfere with the business. A good checklist will usually include the following:
- User password policy that consists of a strong password changed regularly.
- Preventing unauthenticated users from accessing the environment.
- Getting rid of all unnecessary services, drivers, and software.
- Running system updates automatically.
- Documenting all errors, warnings, and suspicious activity.
But those are just the start of things. There are five major components of security hardening, and those are:
- Application hardening
- Operating system hardening
- Network hardening
- Server hardening
- Database hardening
Before you read about the benefits of system hardening, you should know a little more about each of these.
1. Application hardening
This type of hardening is probably the one that most people are familiar with, whether they work in IT or not. Application or software hardening includes things like running security patches, software encryption, anti-virus, firewalls, etc.
But one tactic that only the most security-conscious team is thinking about is limiting or even blocking applications not needed at your company. Allowing even the most innocent application on one of your computers is just another touchpoint or vulnerability to put your company at risk.
2. Operating system hardening
Similar to application hardening, operating system hardening includes things like running automatic security updates. But automatic updates don’t necessarily mean they’re being pushed as soon as the update or patch is released. Installing any update without testing it first could be a nightmare for you and your users. There’s no telling what a software patch could break.
Automatic updates are more about installing these patches without any user interaction — that way, they can’t be skipped or ignored.
Most checklists would also tell you to remove any unnecessary hard drives and make sure the drive with your OS installed is encrypted as well.
3. Network hardening
Your network is going to be one of the bigger, if not the biggest, pain points throughout this entire hardening process.
Perhaps the easiest network hardening techniques include installing and configuring a network monitor and a threat detector. A network monitor will help you keep an eye on all of the traffic on your network, while a detector will look for any outside attacks trying to infiltrate it.
You could also take things a step further and segment your network with subnets so that your office guests won’t have access to internal files or even prevent other departments from accessing files they don’t need.
4. Server hardening
Some of the same techniques used for application and operating system hardening can apply to your servers as well. Basic things like automatically running security patches, using complex passwords, and regulating third-party software that’s installed on them are of value.
However, servers will require quite a bit more security since they’re more of a central point to your environment. You’ll want to disable USB ports and any extraneous network ports.
When it comes to servers, you really only want the people that need to connect to them to have access. Everyone else becomes an extra liability.
5. Database hardening
Now when you’re hardening your databases, there are actually two things you need to look at: the contents of your database and the application managing it. The latter is fairly straightforward, and you’ll use a lot of the same techniques from application hardening. But as you’re looking at how to harden the security of your database contents, there are three things to consider:
- User permissions — think through what users need to access and what level of permission they should have.
- Unnecessary functions — disable features you don’t need or won’t use to help reduce your risks.
- Encrypt the database — secure your contents by making sure your database is encrypted.
Benefits of systems hardening
Keeping your company and its data protected from scammers really should be all the motivation you need. But if it’s not, then maybe working with another company or taking them on as a client will give you more concern. Many companies work with proprietary information, and a leak of their information could be detrimental. That’s just one of the reasons we’re seeing more and more infosec teams cracking down and enforcing stricter policies even with their partners.
Whether you’re here to read up and learn about ways you can use to better your company’s cybersecurity, or you're reading this because you were told you need to harden your security, this is just the start for you. There is a ton of great information out there. Once you dip your toe into the infosec world and start seeing how easy it can be for hackers to gain access to your company’s most sensitive data, I can almost guarantee you’ll want to make some changes.
The most important thing to keep in mind is that this isn’t something you need to overhaul overnight. Security hardening is something that can take some time and probably a little bit of training, too. Be patient with yourself and your team. The best thing you can do is create allies within your company. Communicating and educating about the importance of cybersecurity will get everyone thinking about it and keep it top of mind — that way, you’re not the only person at your company worried about it.