macOS is designed in a way to be virtually flawless, but when rare issues occur, it also comes with tools for troubleshooting. In this article, we will quickly look at how to use one such tool — macOS Traceroute. With Traceroute, you can trace the path any message takes to another device or server as a way of finding out if or where any connectivity issues exist and whether your computer needs fixing. This way, if you diagnose everything at the sending end of a message, you can determine whether the problem is with the recipient or somewhere along the journey that message takes.
What is Traceroute on a Mac?
Traceroute is a way of finding out the exact path a message or transmission takes from one computer or device to another. As Apple explains, Traceroute is designed to follow the path a message takes as it travels through the network from computer to computer.
It almost sounds like something a government spy agency would use. But no, this is something Apple builds into the whole macOS experience. It doesn’t break national data protection laws either, since IP addresses — unless people or companies protect and mask them — are effectively like phone numbers. Remember, they’re built on the same principles, so any accessible — unmasked — IP address and related details are publicly accessible.
How to use macOS Traceroute?
There are two ways you can do this — either through Terminal for all macOS versions or Network Utility (for macOS versions older than Big Sur).
1. Run Traceroute through Terminal
- Search for Terminal (either via Spotlight Search or Applications > Utilities).
- Open Terminal.
- Within Terminal, enter the following command:
traceroute hostname
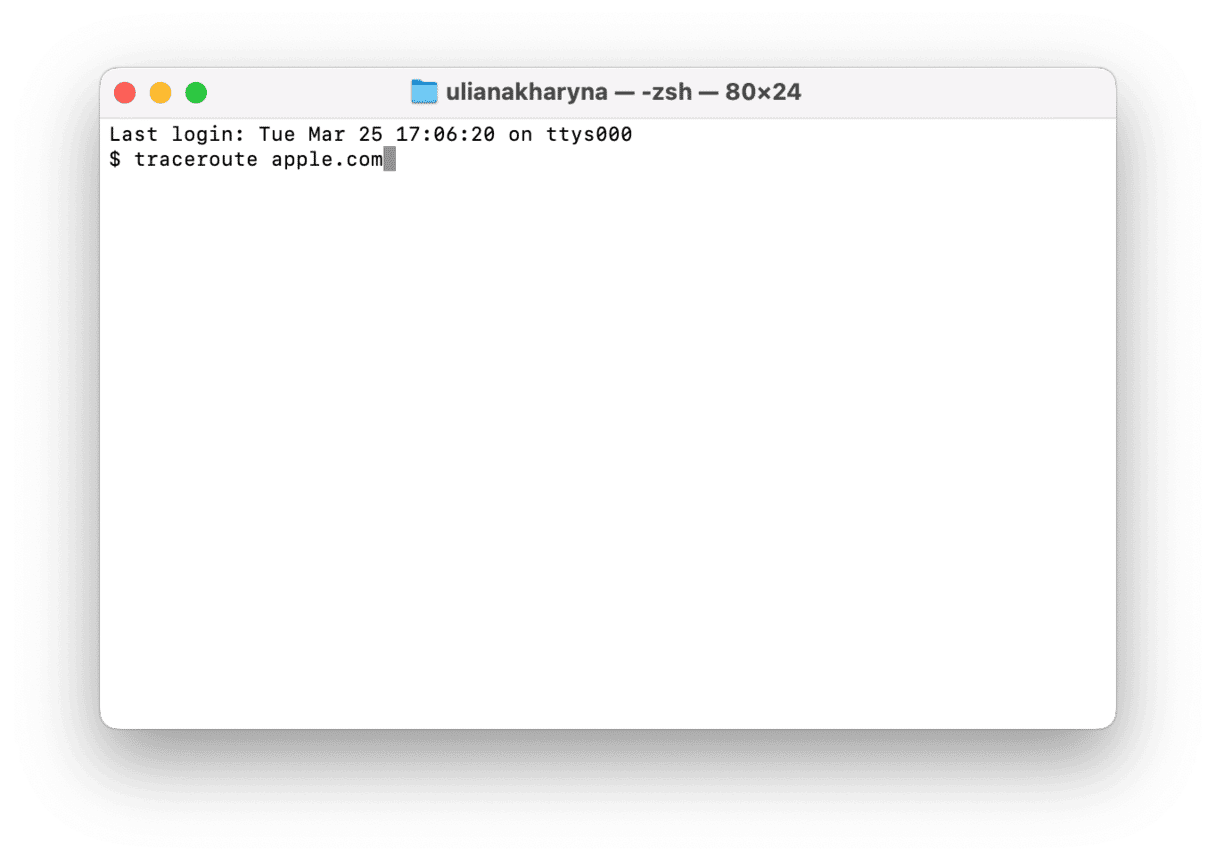
‘Hostname’ could be the domain or URL of the destination that you want to trace or the IP address of a server or device. If you are entering a website address, you don’t need to use www. or https://. Simply input the address with the relevant domain ending, such as .com
Always leave a space between traceroute and the address you are trying to search for. Now, it will probably take a few minutes.
It should then give you a list of connections between your Mac and the destination address. If you see the * symbol, it means the search has timed out. It may need to be attempted again, or the search isn’t possible. The latter might indicate connectivity problems en route or protected addresses that prevented the search from going further.
Another way to do this is through the Network Utility macOS app.
2. Run Traceroute through Network Utility
- For Mac devices running anything prior to Mojave, you can find Network Utility in Applications > Utilities. On other macOS versions older than Big Sur, search it through Spotlight.
- Now, go to the Traceroute tab.
- Enter the domain or URL of the destination that you want to trace or the IP address of a server or device.
- Click Trace to start the search.
- This will probably take a few minutes. It should then give you a list of connections between your Mac and the destination address.
How effective your searches are — regardless of the method used to access Traceroute — will depend on Internet speeds and connectivity. If your Internet isn’t working as it should, there is quite a bit that can be done with the right tools.
Want to speed up the Internet on your Mac?
With a Mac and the right tools, you have a lot of control over how fast — or not — you experience the Internet. It isn’t only a problem your network provider can fix. You can manage a lot of this yourself with a simple and easy-to-use tool.
To figure out how to get faster Internet speeds, download CleanMyMac (get your free trial here).
Use the Menu App to show your current Internet speeds (upload and download). To do it, click the iMac icon from the menu bar, find the tab under Battery (one with the Wi-Fi icon), and hit Test Speed.
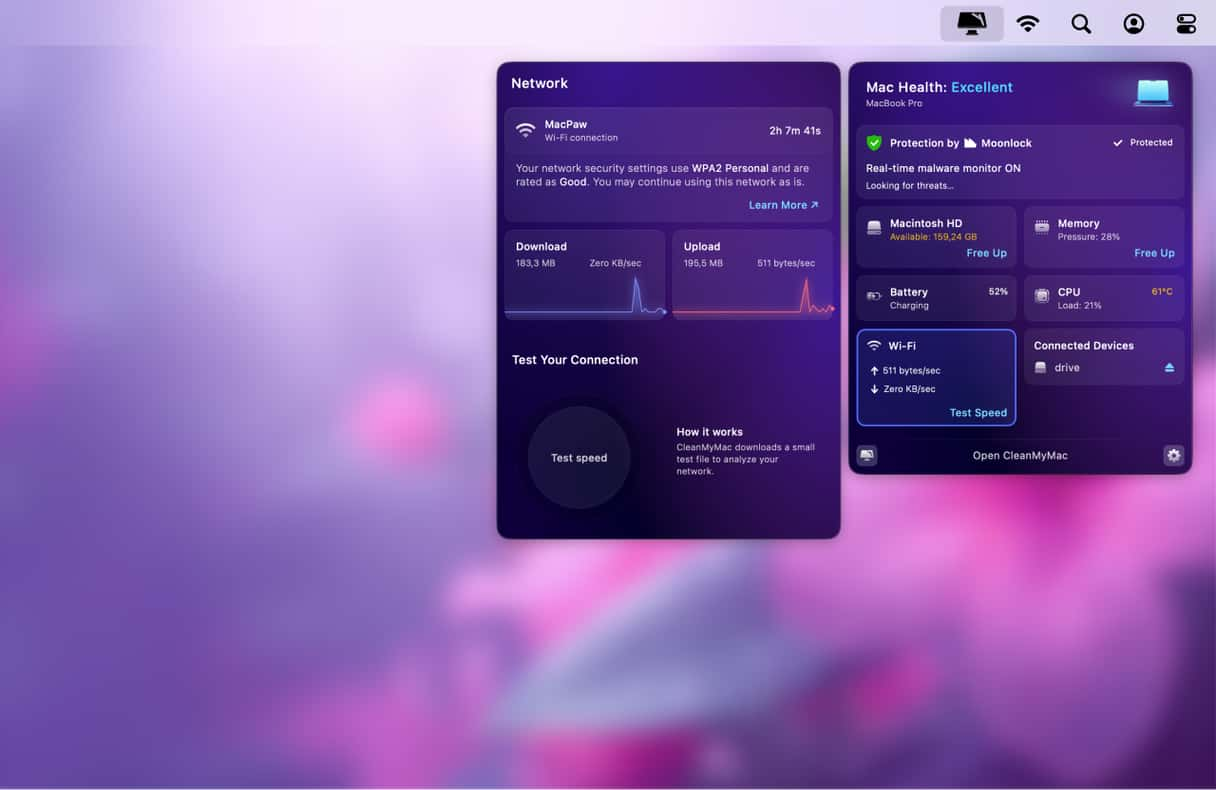
If this isn’t where you need it to be, there are a few things you can try:
- Use the Protection feature in CleanMyMac to clear out old Internet data.
- To pick up even more speed improvements, use the DNS cache tool to enhance your Mac’s connectivity. You can find it within the Performance feature.
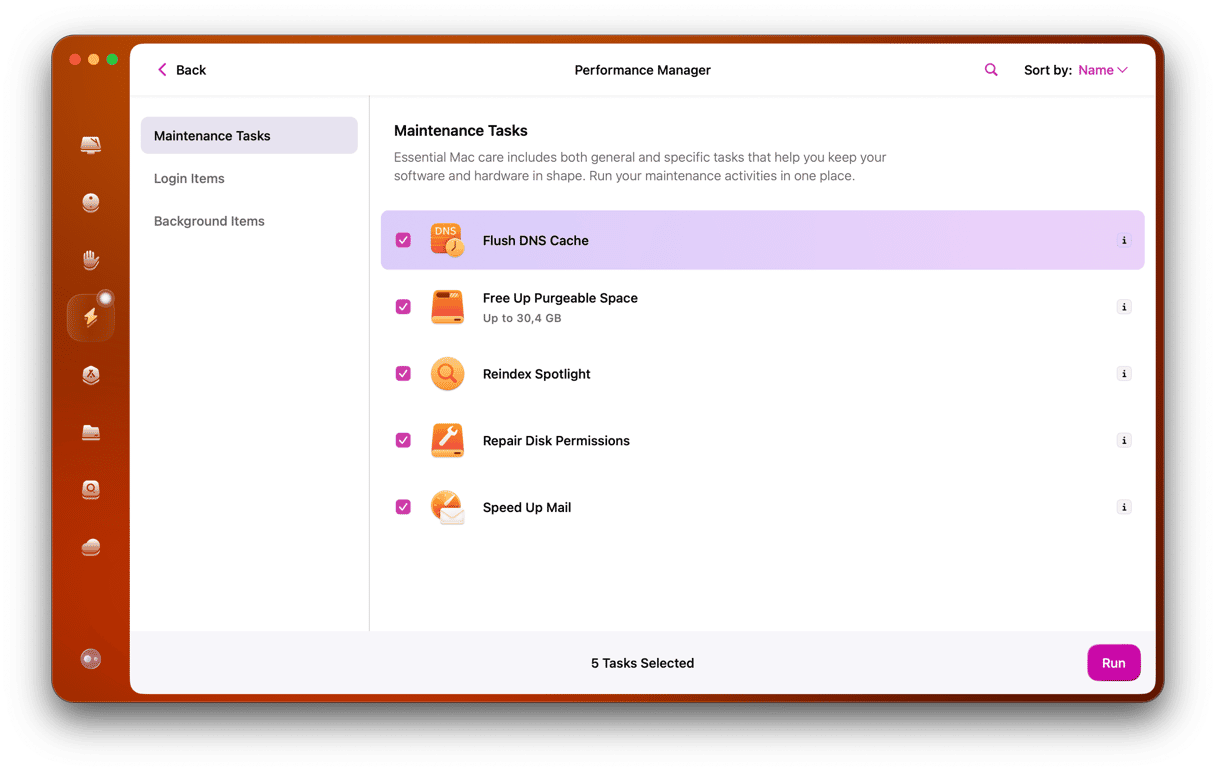
CleanMyMac is a really useful Mac performance improvement app. It is an easy-to-use app that includes a whole load of features that improve how a Mac runs, including its network and browser connections, so you can be sure that it is running as smoothly as possible.
Now, you know what Traceroute is and how to use it on both old and new macOS versions. Remember, though, to always double-check commands you run in Terminal to avoid system corruption. Thank you for reading and happy browsing!