When it comes to our computers and operating systems, sometimes the best and most helpful features can be exploited by a scammer. A perfect example of this is the macOS process called NSURLSessionD. Even though its main purpose is to run in the background, hackers can use this to update your browser settings or even upload private information.
So, what do you do if you find out NSURLSessionD is working overtime on your Mac? Well, you’re in the right place. This article explores the different ways a browser hijacker can infect a Mac, the symptoms to look out for, and the steps you can take to protect your Mac from malicious software.
| Name | NSURLSessionD |
| Category | Browser hijacker |
| Symptoms | Slow performance |
| Infection method | Corrupted databases and malicious file downloads |
| System damage | Overheating and maxed-out CPU usage |
| Removal | Manual removal |
What is NSURLSessionD?
The tricky thing about NSURLsessionD is that it is a legitimate process in macOS. It’s a daemon process on macOS and iOS that is responsible for handling tasks, such as caching, cookie storage, and redirect handling, among other things. It is also responsible for handling background transfers and downloads.
Simply put, it’s a process that runs in the background to help sync your Mac with other services. The most popular one is iCloud.
However, browser hijackers can exploit this process and use it to max out your computer’s performance. Additionally, it can be a security risk because hackers can use this daemon to steal your personal data.
How does a Mac get infected with NSURLSessionD?
The most common response when someone finds out they have malware or a browser hijacker on their Mac is to say, “I thought Macs couldn’t get viruses.” While it’s true that macOS is secure in a lot of ways, it’s not perfect.
Software bundling is a frequently used method where malicious software is installed. A user may unknowingly download and install software that contains a browser hijacker. This can happen when downloading software from untrusted websites or when clicking on malicious links in emails or on social media.
A browser hijacker can also be installed on a Mac when a user visits a compromised website. Once a user visits the website, the browser hijacker can be automatically downloaded and installed without the user’s knowledge.
Lastly, deceptive pop-up ads are also a common tactic that scammers use to trick people into installing their malicious software. They’ll design pop-ups to look like system notifications or virus alerts and prompt users to download their malware.
So, why does NSURLSessionD use high CPU or memory?
NSURLSessionD is a legitimate Apple process and may use high CPU or memory when something slows down and causes congestion in the system. This could be caused by syncing massive files to iCloud, buggy apps, timeout loops, and not being able to reach iCloud servers.
However, from a malware point of view, a browser hijacker piggybacking on NSURLSessionD on a Mac can feast on your CPU and memory due to the large amount of data it copies and steals.
Since it needs to move data to an external server, this puts an intolerable strain on your MacBook and Wi-Fi connection. This, in turn, will increase CPU and memory usage and eventually lead to the network and your device slowing to a crawl and then crashing.
This is quite a serious problem. If your MacBook is overworked, the battery can overheat, which may lead to potential damage to the battery and any other internal components. Therefore, it should not be ignored.
How can NSURLSessionD harm my Mac?
NSURLSessionD itself can’t harm your Mac, but it can be exploited by browser hijackers that can. Because NSURLSessionD is used to manage cache, cookies, and syncing files with your browser, there’s a lot it can do to your computer.
The daemon can be used to reset your browser settings, lock down your homepage, and redirect links. But perhaps the scariest bit is that it can be used to sync your private data with an unknown cloud server, thus stealing your information and leaving your Mac vulnerable to other attacks.
How to remove NSURLSessionD from Mac manually from different browsers
It’s important to keep in mind that NSURLSessionD is a daemon that’s built into macOS. So, that means removing it isn’t really an option. You actually want to get rid of the browser hijacker that is exploiting it instead.
Don’t worry; it’s probably not as difficult as it might sound. There are a few steps, but as long as you follow these, you should be all set.
How do I stop NSURLSessionD on Mac
Since this is a daemon and not a full-blown app, simply hitting Command+Q on your keyboard won’t quit it. Here’s what you’ll need to do:
- Open a new Finder window.
- Click Go > Utilities.
- Open Activity Monitor.
- Select NSURLSessionD.
- Now, click the X button and follow the prompts to force quit it.
Lower NSURLSessionD CPU usage using the Terminal
Since NSURLSessionD is a legitimate Apple Mac and iOS process, you can’t permanently disable it. However, you can temporarily shut it down for the purpose of removing any browser hijacker on your MacBook.
Simply open Terminal and type the following:
sudo killall -9 NSURLSessionD
You can also temporarily kill the process by disabling iCloud background sync. Just don’t forget to re-enable it later to back up your data.
Next, enter:
defaults write NSGlobalDomain NSDocumentSaveNewDocumentsToCloud -bool false
Then:
killall Finder
Sometimes, NSURLSessionD can simply get clogged up with DNS and cache issues. Enter:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Then:
rm -rf ~/Library/Caches/*
Finally, you can throttle NSURLSessionD using this command:
sudo renice +20 -p $(pgrep NSURLSessionD)
As we said, a lot of these are temporary fixes. For a more long-term solution, you need to solve the underlying cause rather than slapping a band-aid on it.
Remove browser extensions
The next thing you’ll want to look for is any suspicious browser extensions that might be installed. It’s crucial to check all of the browsers you have installed and not just your default one. A browser hijacker that’s left lurking on your Mac is likely to spread to your other browsers next time it’s in use.
Safari
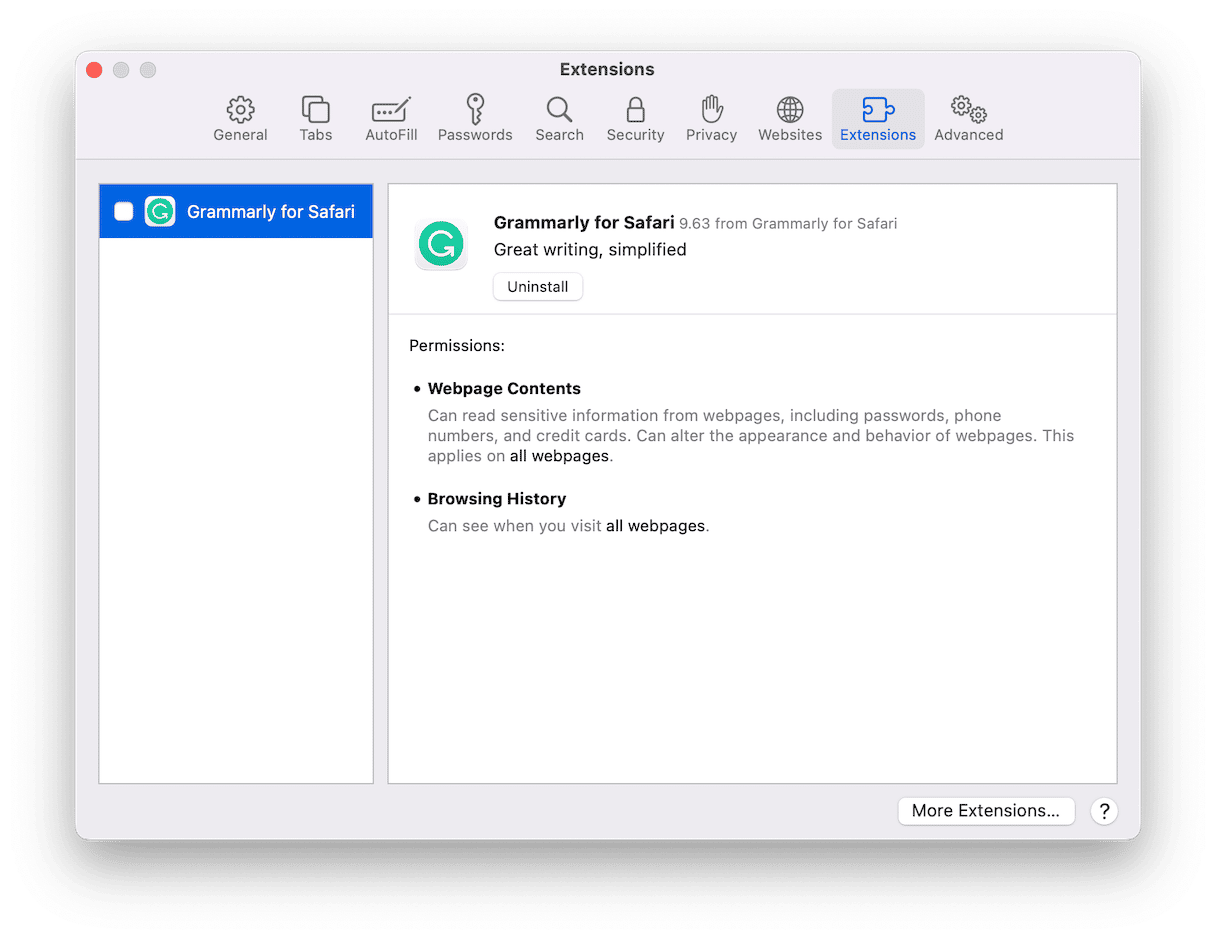
- Click Safari > Settings > Extensions.
- Search for any suspicious extensions.
- Select the extension > Uninstall.
- Now, quit Safari.
Chrome
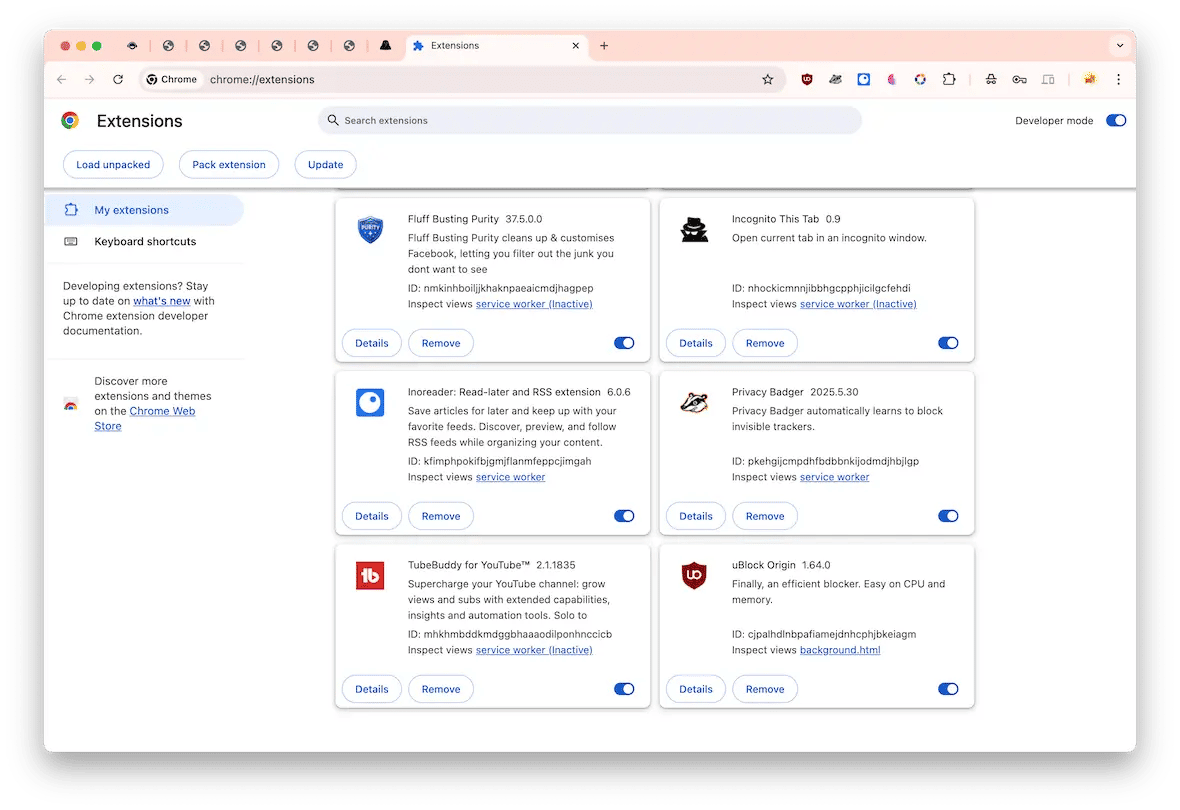
- At the top of the browser, click through Chrome > Settings > Extensions.
- Look for any odd extensions, then click Remove next to them.
- Close Chrome.
Firefox
- In Firefox, click three lines > Add-ons and themes > Extensions.
- Scroll until you find any strange extensions.
- Click … > Remove.
- Then, quit and restart Firefox.
After you do all of that, it’s best to go ahead and restart your Mac. This gives all of the software on your computer an opportunity to start fresh.
How to prevent infecting a Mac with browser hijackers
A browser hijacker is fairly low on the list of most dangerous malware. It doesn’t spread like a virus, so it is self-contained and easily removable by antimalware tools.
However, like all types of malware, browser hijackers are still dangerous. They should never be tolerated or ignored. You’ll regret it later.
The best tool to disable NSURLSessionD malware is Moonlock. It’s a lightweight, fast, and powerful platform that catches malware automatically with its real-time protection feature, and everyone should have it on their Mac to keep it safe.
Start your Moonlock plan (it’s free for 7 days), open it up, and its real-time protection can already detect and neutralize any malware that’s active on your Mac.
If Moonlock doesn’t alert you at once, do the following easy steps to ensure the NSURLSessionD browser hijacker isn’t hiding deep in your system:
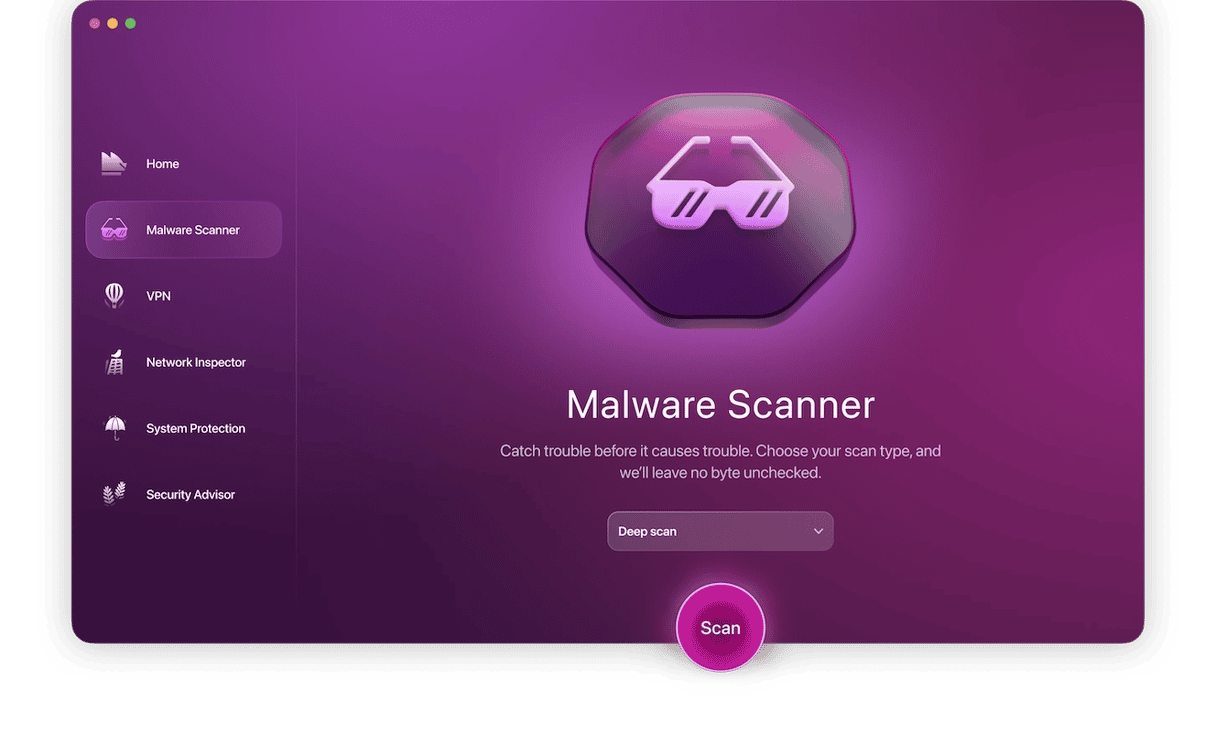
- Go to the left sidebar and select Malware Scanner. This is a thorough on-demand malware removal tool.
- Choose your scan type. We recommend using Deep.
- Click the Scan button. This will begin a thorough malware search through your MacBook. Moonlock will search for and catch all traces of the browser hijacker, as well as any other hidden threats on your device.
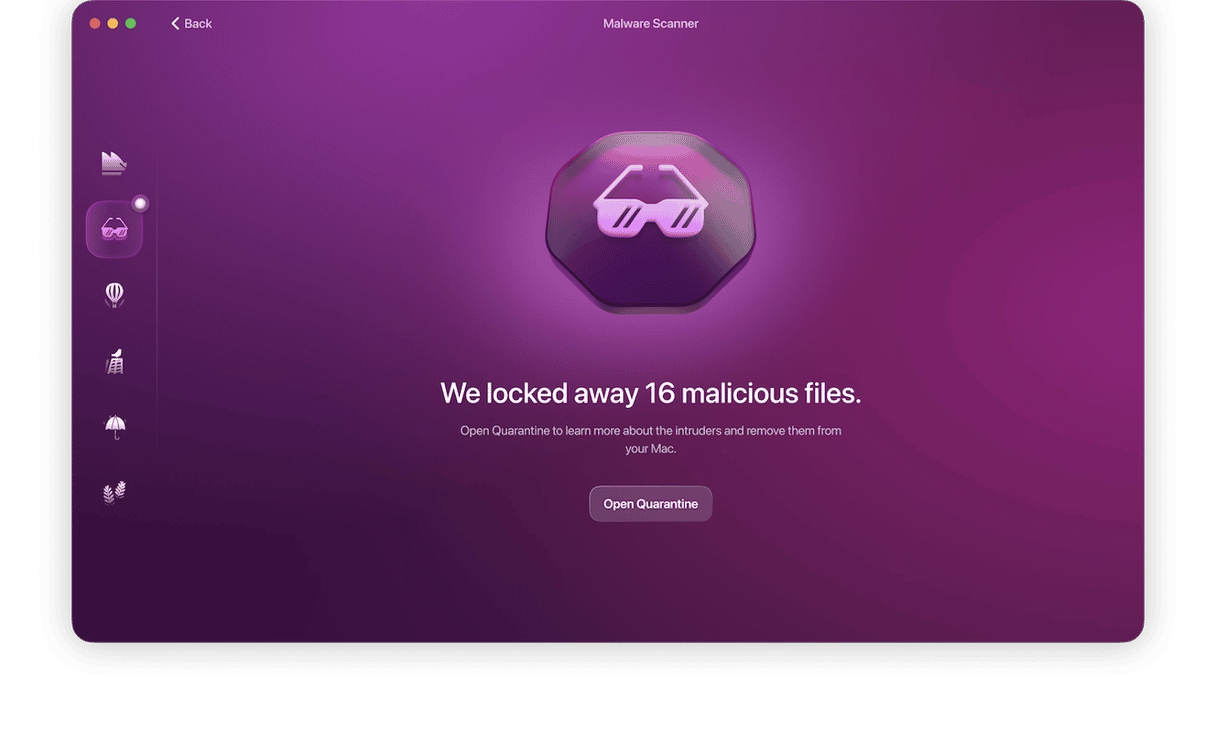
- When the browser hijacker has been found, Moonlock will lock it up in Quarantine. From there, malware can’t affect your Mac processes anymore and can only wait for you to remove it.
- Open Quarantine, select everything that’s in there and remove. All threats will be wiped out, with just a record left in the Removed Malware log.
Remember to be careful and always on alert when you’re browsing the internet. It’s also a good thing to take note of your browser settings and be suspicious when they change. Mac computers are also vulnerable to browser hijackers, and it’s important to be aware of the ways in which these malicious programs can infect your device.
Hopefully, after reading this article, you’re feeling more empowered to protect your computer from other browser hijackers. And you can start using Moonlock to keep your Mac safe.