One of the great advances on the web in the last decade or so is one that many people haven’t noticed is the implementation of HTTPS and the improvement in security it brings for web browsers. HTTPS is a secure version of the HTTP protocol that enables websites to connect to each other and allows us to surf the web. Modern browsers won’t connect to sites that don’t use HTTPS or whose security certificate is out of date or not valid. When that happens while you’re using Safari, you will see an error message that says, ‘Safari can’t establish a secure connection to the server.’ In this article, we’ll explain why that happens and what you can do about it.
What does ‘Safari can’t establish a secure connection’ mean?
At its most basic, the error message means that Safari doesn’t trust the website you’re trying to visit. But why can’t Safari establish a secure connection? That could be for one or more of a number of reasons, including:
- Safari is unable to find the website’s security certificate.
- The security certificate is out of date.
- The security certificate is invalid.
- DNS records are incorrect.
- Cache data on your Mac is causing Safari to think the website is insecure.
- There’s another problem with the certificate or website security that leads Safari to conclude it can’t trust it.
The website is there and functioning, and you may be able to access it in another web browser. But Safari has specific security standards that websites need to meet, and if you see that error, it usually means the site doesn’t meet those standards.
However, it’s possible that, in some cases, the problem isn’t with your website and that Safari has got it wrong. We’ll show you below how to check that and fix it if necessary.
How to fix ‘Safari can’t establish a secure connection’ on Mac
The first thing to do is to try another web browser. If that browser can connect, the problem could be with Safari, and you might be able to fix it. However, it could also mean that the website meets the security requirements of the other browser but not Safari. If you can’t connect to the website in any browser, there is a problem with the site’s security. That could mean the website is dangerous. If you’re sure it’s safe, you could try contacting the site owner and telling them that it’s inaccessible.
1. Check the web address
Look carefully at the URL of the website you’re trying to visit. Is it correct? One major form of malicious web activity is websites that impersonate other websites using URLs that are very close to the real URL. So, make absolutely sure the URL you have typed or clicked on is correct.
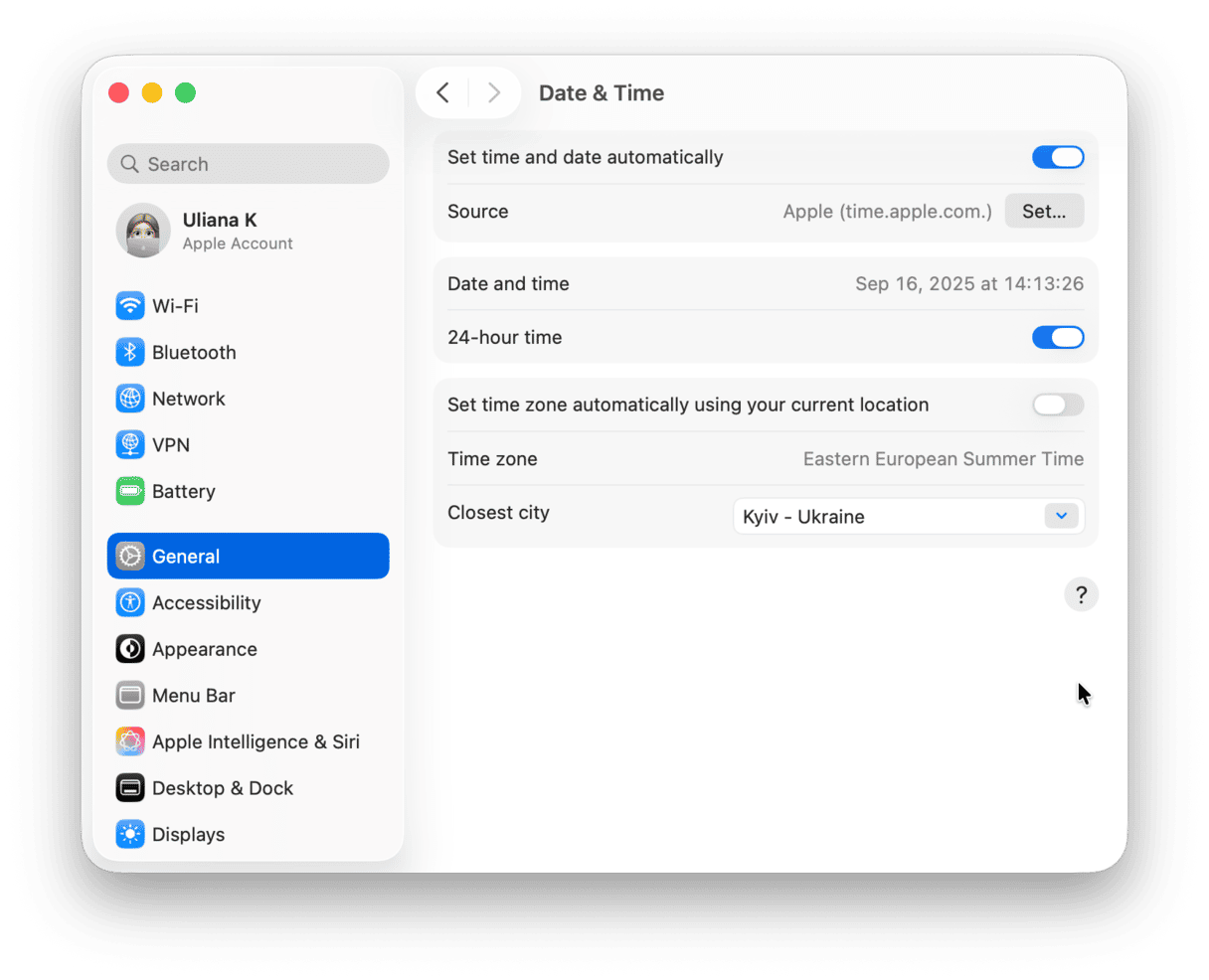
2. Check the date and time on your Mac
If the date and time on your Mac are incorrect, that can cause lots of problems when you try to go online because the time on your Mac won’t match that on the remote server, and Safari may assume that that indicates a problem with the server. Go to System Settings > General > Date and Time and check it’s correct. Unless you have a good reason not to, you should turn on Set Time and Date Automatically and set the Source to Apple.
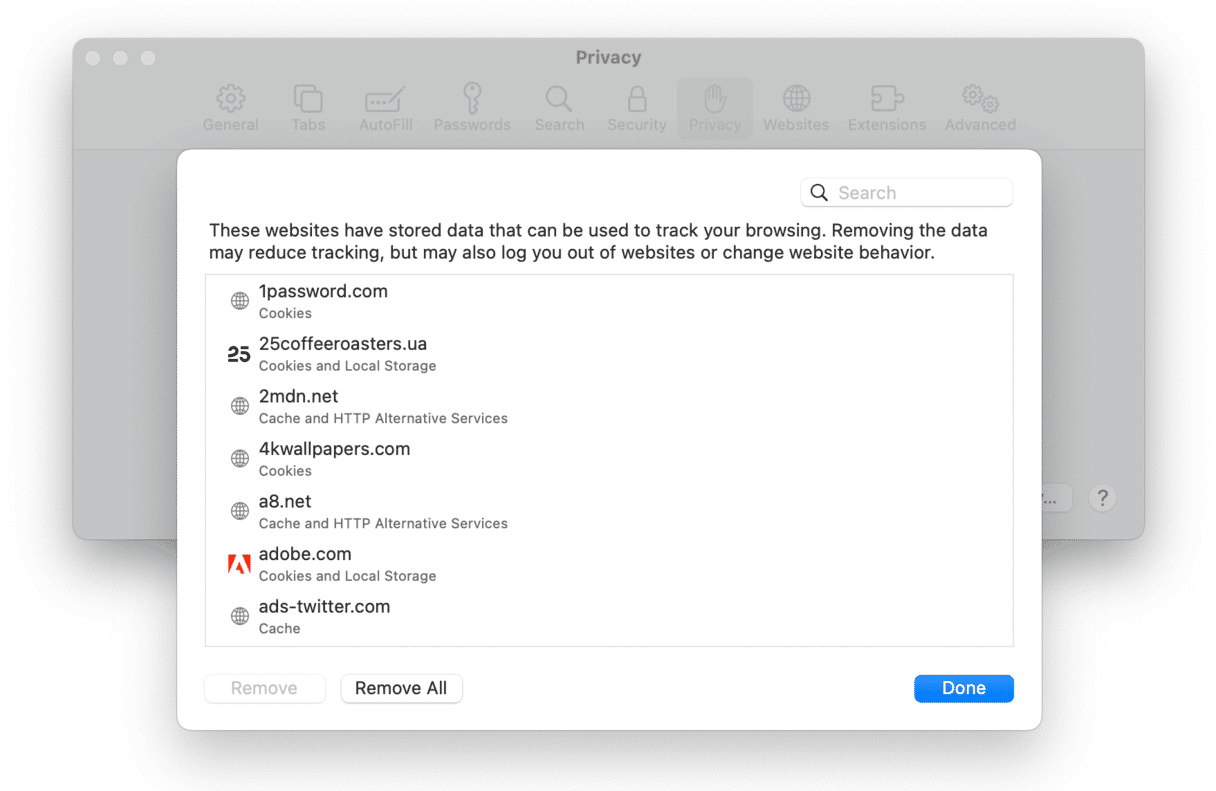
3. Clear browser cache
It’s possible that there are cache files on your Mac associated with the site you’re trying to visit that are causing Safari to think that the site is not secure. So, it’s a good idea to clear the cache.
- Click on the Safari menu and choose Settings.
- Choose Privacy.
- Click Manage Website Data and wait for it to load.
- Click Remove All.
4. Change DNS servers
When you type or paste a URL into Safari or any web browser or click on a link, your Mac checks the URL against a domain name system (DNS) server and uses that to obtain the IP address of the website so it can connect to it. By default, your Mac uses the DNS server configured by your broadband provider. If the DNS server is down or its records are not up to date, that can cause problems when you try to connect to the internet. And it could make Safari think a site is insecure. To test this and fix it, switch to a different DNS server. Google has free DNS servers you can use.
- Flush your Mac’s DNS cache (see Tip above).
- Click the Apple menu and go to System Settings > Network.
- Choose your Wi-Fi network, then click Details.
- In the DNS section, select the current DNS server.
- Click the ‘-’ to remove it.
- Next, click the ‘+’ to add a new DNS server. Type:
8.8.8.8. - Click the ‘+’ again and type:
8.8.4.4 - Click OK and quit System Settings.
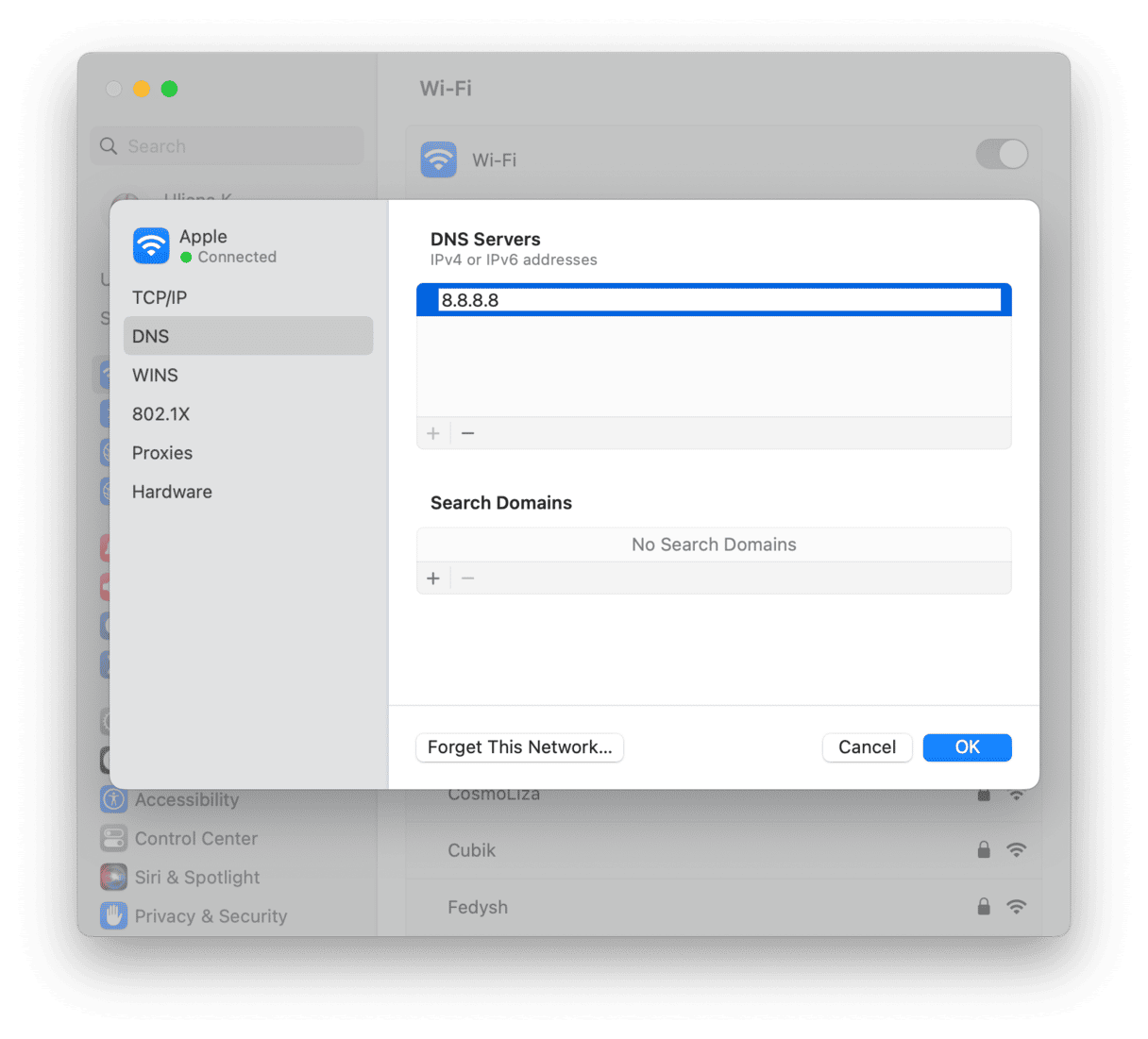
Your Mac will now use Google’s DNS servers to obtain the IP address of websites it needs to connect to. Try to connect to the website again. If it works, you’ll know the problem was with your broadband’s DNS server.
5. Check your browser extensions
If you have lots of extensions installed in Safari, one of those could be causing a problem that leads Safari to think a website is insecure. This is especially so if browser extensions are out of date. To check whether a browser extension is causing the problem, disable all browser extensions in Safari and try to access the website again.
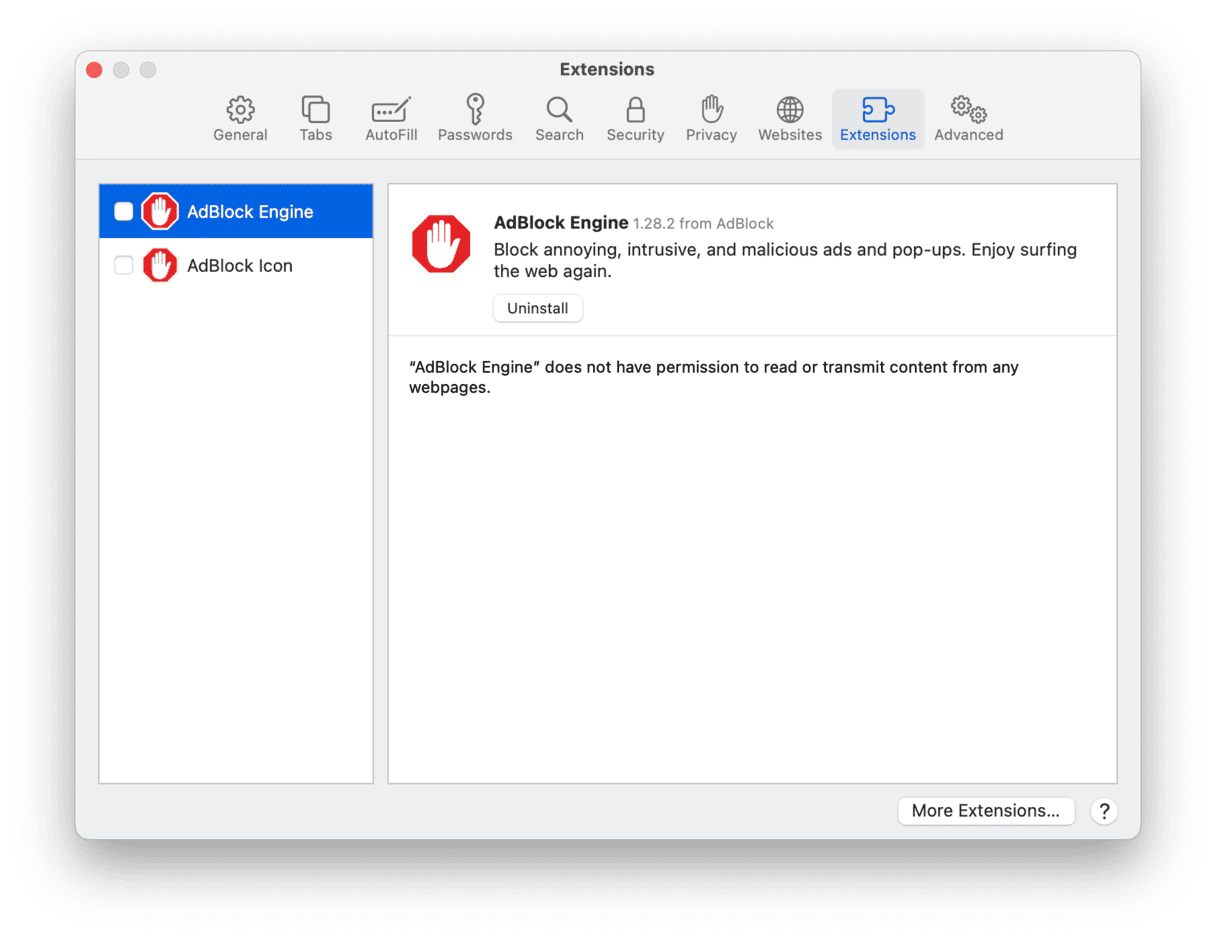
- Click the Safari menu and choose Settings.
- Select Extensions in the bar at the top.
- Choose each extension in turn and deselect the box next to it.
- Quit and reopen Safari and try to go to the website again.
6. Tell keychain to trust the website’s security certificate
One of the reasons you will see the ‘Safari can’t establish a secure connection’ error is that there is an issue with the website’s security certificate, which means that Safari can’t read it or thinks it is invalid, perhaps because it’s out of date. If you’re sure the site is safe, you can tell Safari to trust the certificate using Keychain Access.
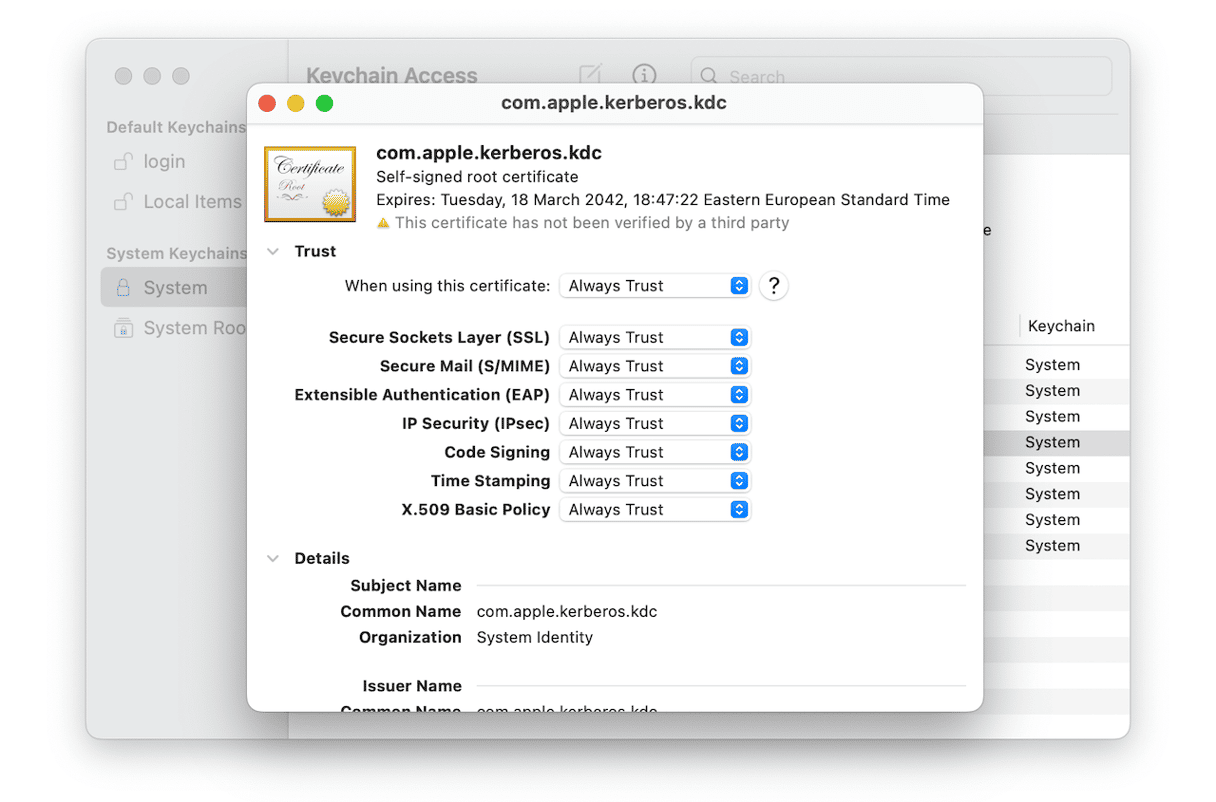
- Go to Applications > Utilities and open Keychain Access.
- Choose System in the sidebar, then All Items in the toolbar.
- Look for the website’s security certificate in the main window. If you can’t find it, try clicking Certificates in the toolbar.
- Double-click the certificate.
- Click the down arrow next to Trust.
- Choose Always Trust from the ‘When using this certificate’ menu.
- Quit Keychain Access and try to open the website again.
7. Reset Safari
Resetting an application returns it to the state it was in when you first installed it. In the case of Safari, that means when macOS was first installed on the computer, or an update that included an update to Safari was last installed. To reset an application manually, you would have to remove all the settings and supporting files, as well as user data, that it has placed on your Mac. However, CleanMyMac can do it for you.
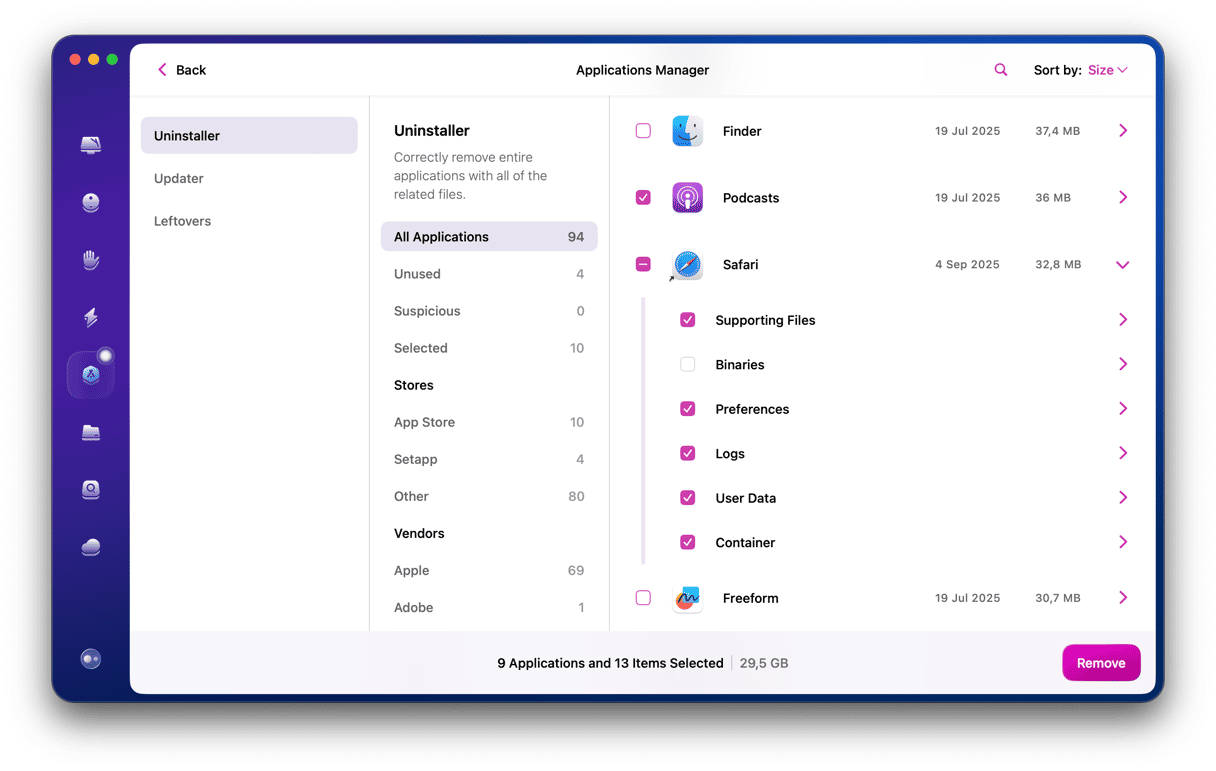
- In CleanMyMac, choose Uninstaller in the sidebar and click Apple in the middle pane.
- Locate Safari in the window at the right and click the drop-down arrow next to it.
- Select the Container box.
- Click the dropdown menu next to Safari and choose Remove.
- Click the Remove button.
If you don’t see Safari on the list, open CleanMyMac Settings from the menu bar. Go to Ignore List > Uninstaller and deselect Ignore System Applications. Now, follow the steps outlined above to reset Safari.
Safari is a great web browser, and one of its best features is security. As with all Apple software, security and your privacy are at the top of the list of priorities. That means that Safari errs on the side of caution when it comes to connecting to websites that may not be secure. And the result is the error message ‘Safari can’t establish a secure connection.’ Safari won’t take you to the website because it doesn’t meet Safari’s security standards. If that happens to you, follow the steps above to identify the cause of the problem and fix it.