When it comes to error codes on the Mac, some are more common than others. And one of the most common is error code -43. That code is usually accompanied by a message saying that a task you’re trying to perform can’t be completed because one of the files needed for the task can’t be found. There are a number of reasons why the error may occur, and so there are a number of different ways to fix it. We’ll take you step by step through the process of troubleshooting error code -43.
What is error code -43 on Mac?
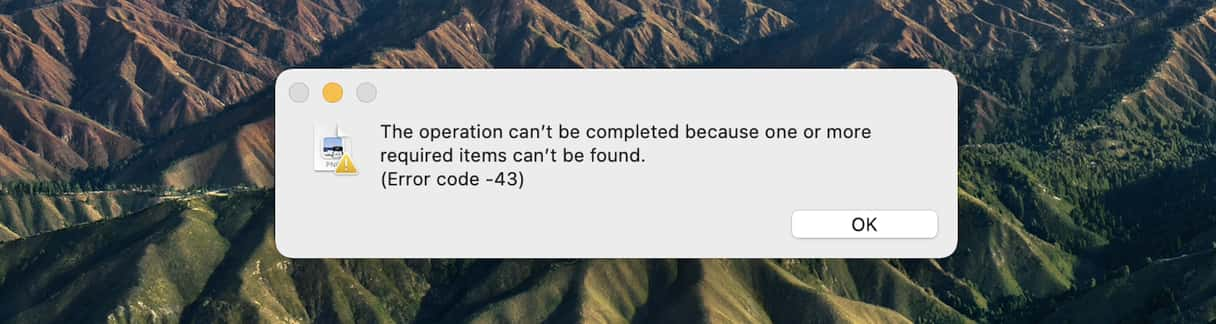
Error code -43 relates to the macOS Finder being unable to find a file it needs to carry out a task you’re trying to perform. Obviously, if it can’t find the files, then it can’t complete the task, so it displays an error.
What causes error code -43?
There are a number of different possible causes.
- The file could have been moved or deleted.
- The file could still be in its original location but has become corrupted.
- The volume on which the file is stored may have unmounted as well as be inaccessible or even damaged.
- The Finder could have a problem.
- There may be a problem with the file directory on the disk on which the file is stored.
How to fix error code -43 when you see it
As with most problems using a computer, fixing this one is a matter of eliminating possible causes one at a time, starting with the most likely and the fixes that will be least disruptive.
1. Check that the file you’re working with is complete
Sometimes, when you copy a file from another location, like a network server, or download it from the internet, the process doesn’t complete properly, and the file is incomplete. It looks like it’s there in the Finder and may even have the correct icon. But the data in the file is damaged. The easiest way to check this is to navigate to the file in the Finder and select it. In the information section in the preview window, it will display the file size. If the size is 0 bytes, it hasn’t been copied properly. The solution is to delete that version of the file and copy it again from the source.
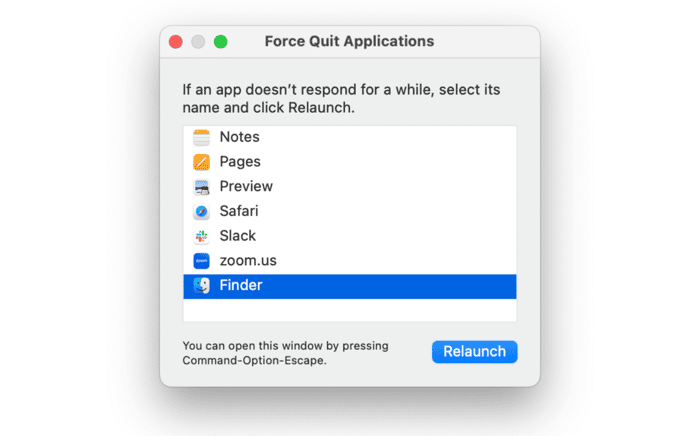
2. Force restart the Finder
This is the simplest possible solution and so it makes sense to try it first. Press Command+Option+Escape. When the Force Quit window appears, select the Finder and click Relaunch. Wait for the Finder to restart, then try to perform the same task as you were when you got error -43.
3. Check the disk in the Finder
If the volume on which the file you’re trying to work with is stored is on an external disk or USB stick, check in a Finder window sidebar to make sure it’s still mounted. If not, try unplugging it and reconnecting it. If that doesn’t work, go to Applications > Utilities and open Disk Utility. Select the disk and click Mount in the toolbar.
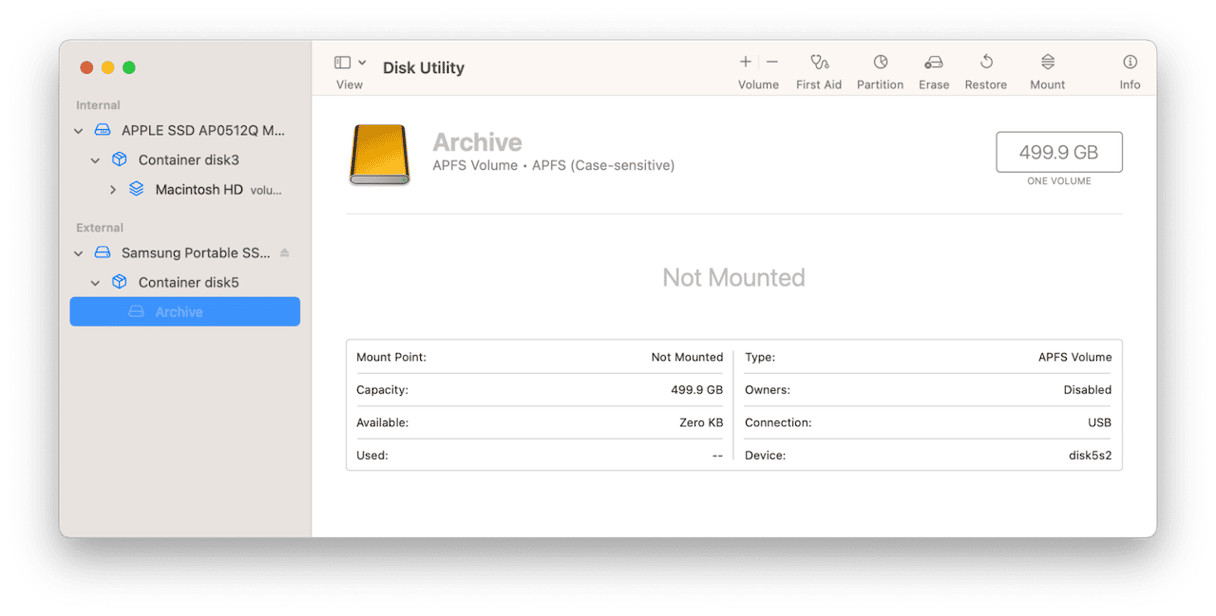
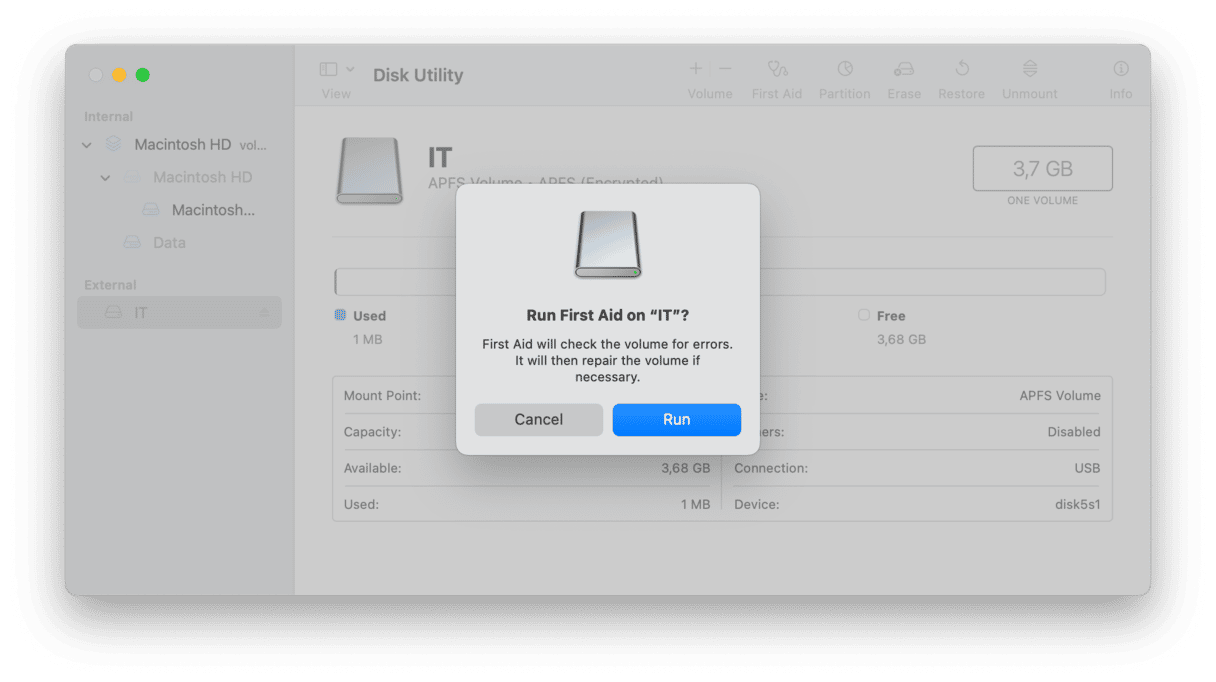
4. Repair the disk
If the disk still won’t mount, select it in Disk Utility and click First Aid. Follow the instructions on the screen to check the disk and repair any problems.
5. Boot your Mac into safe mode
When you boot into safe mode, your Mac loads only the extensions it needs to run basic functions and performs a check on the startup disk, repairing any problems. The process for restarting in safe mode is different depending on whether you have an Apple silicon or Intel-based Mac.
Apple silicon
- Shut down your Mac.
- Press and hold the power key until you see ‘Loading startup options.’
- Choose your startup disk.
- Press Shift and choose Continue in Safe mode.
- Wait for your Mac to restart. You should see ‘Safe Boot’ in the menu bar

Intel
- Restart your Mac while holding down the Shift key.
- Release the Shift key when you see the login window.
- Log in to your Mac. If you’re asked to log in a second time, do that.
- You should see ‘Safe Boot’ at the top of the login window the second time.
Once you have started your Mac in safe mode, try to complete the task that caused error code -43.
6. Use Terminal
If you were trying to empty the Trash when you got error -43, you can try forcing it to empty using Terminal:
- Open Terminal from Applications > Utilities.
- Type sudo rm followed by a space (don’t press Return yet).
- Click on the Trash in the Dock to open it.
- Drag the files you want to delete into the Terminal window.
- Press Return.
- Enter your password and press Return once again.
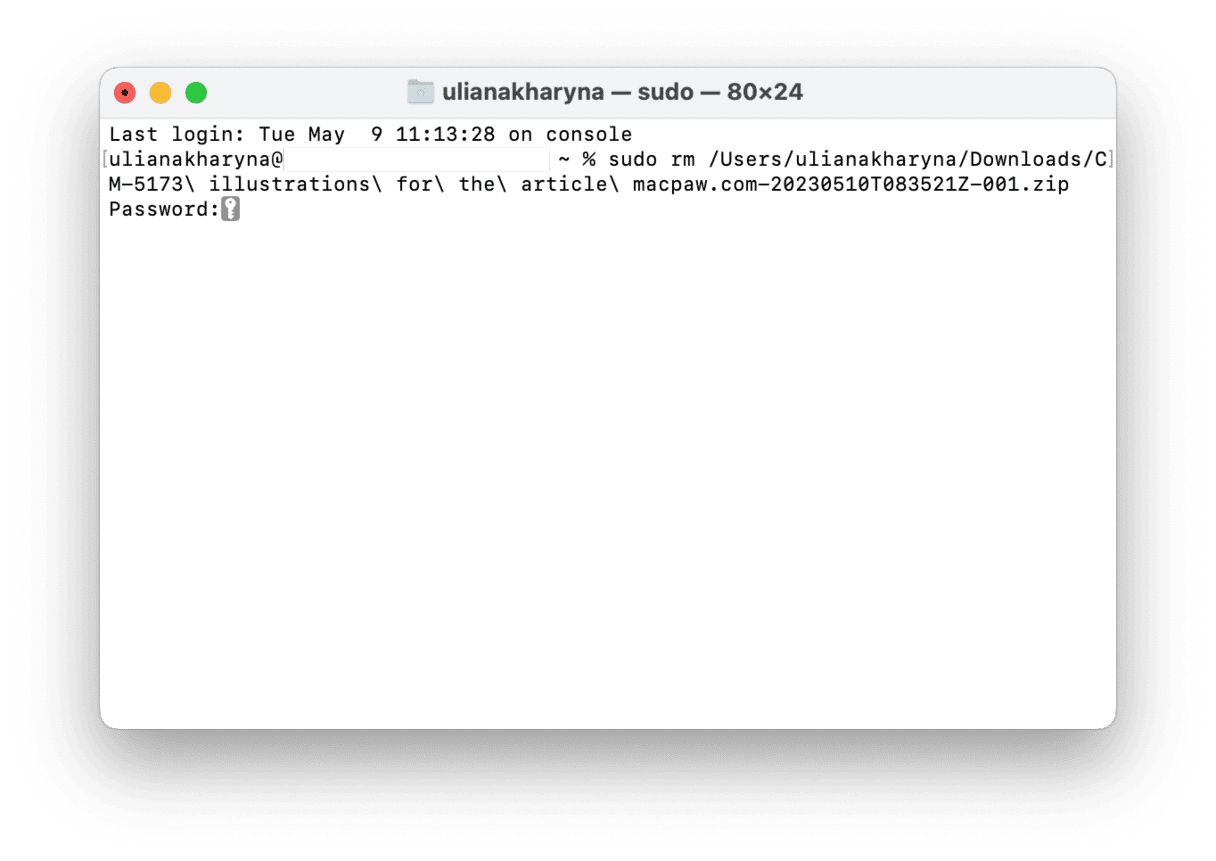
Important: Use this method with caution, as you won’t be able to restore the files you deleted.
Error code -43 usually means that the Finder can’t find a file that you want to use or empty the Trash. It could be caused by a number of things, including the file being missing or corrupt or a problem with the disk directory. Follow the steps above to identify and fix the problem.