Whatever you do on your Mac, there are lots of processes running in the background to make sure everything works as it should. Even tasks as simple as moving a file from one folder to another or writing a sentence in a text editor need several processes to complete. The more complex a task, the more processes are needed. Most of the time, we never need to think about those processes. Until something goes wrong. And one of the things that can go wrong is a task starting to hog system resources like CPU cycles or memory. In this article, we’ll show you what to do when one of those processes, VTDecoderXPCService Mac process, has high CPU or memory usage on your Mac.
What is VTDecoderXPCService on Mac?
VTDecoderXPCService is a part of Apple’s Video Toolbox, a set of tools that allows Apple and third-party applications to use your Mac’s GPU to decode and encode video. VT stands for Video Toolbox. The Decoder bit explains that it’s responsible for decoding video. Finally, XPCService refers to Extensible Process Protocol — the bit that communicates with applications. So, for example, if you watch a video in a web browser, whether it’s Safari or a third-party browser, VTDecoderXPCService will enable your Mac’s GPU to decode the video. And if you export a video in Final Cut Pro, VTEncoderXPCService will be involved in encoding it.
Why does VTDecoderXPCService have high CPU and memory usage?
The resources VTDecoderXPCService uses on your Mac will be dependent on the video you are trying to watch. A 4K HDR video, for example, demands more from your Mac’s GPU than a 720p non-HDR video. However, under normal circumstances, no video should use so many resources that your Mac slows down or becomes unstable. If it does, that could indicate an issue with macOS or with a third-party app or process.
How to check if VTDecoderXPCService has high CPU or memory usage
Before trying to fix the issue, it’s a good idea to make sure we know what’s causing that. We can do that with Activity Monitor.
Just follow these steps:
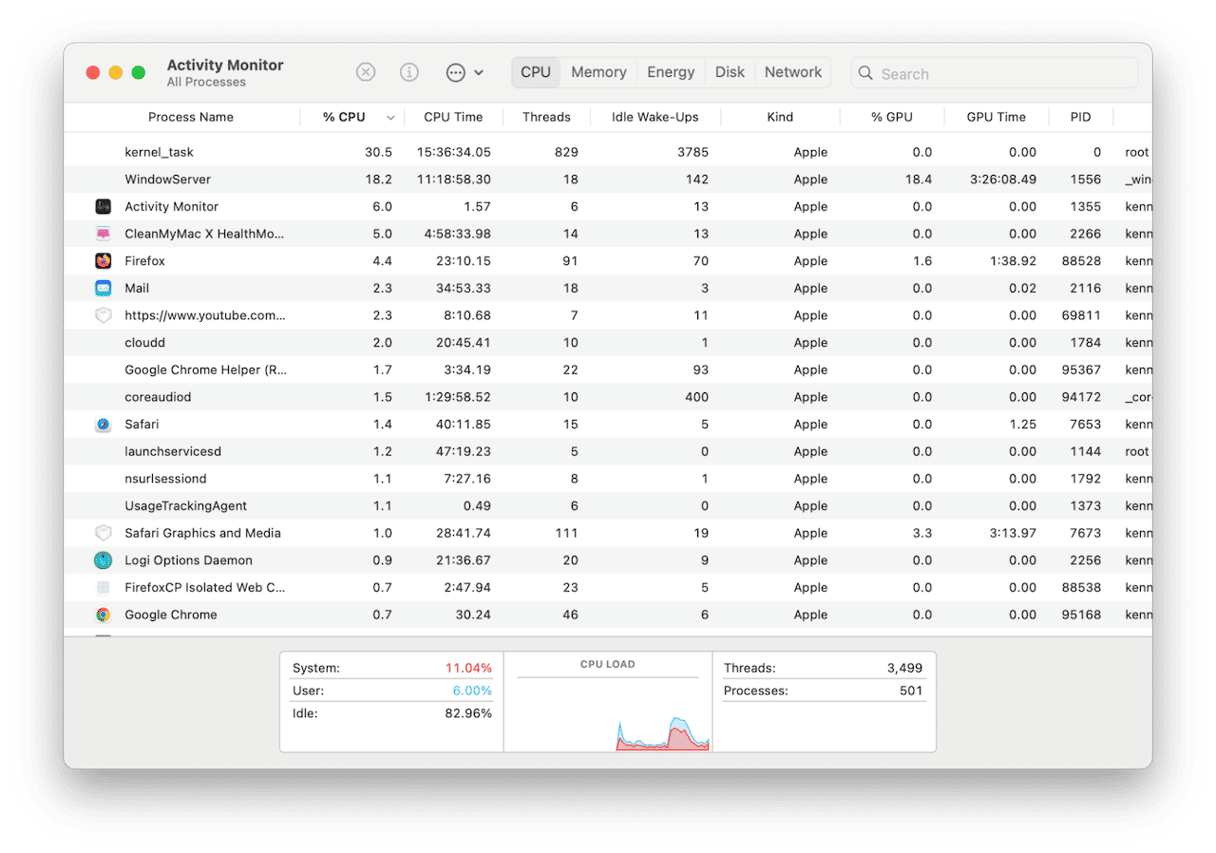
- Go to Applications > Utilities and double-click Activity Monitor to open it.
- Choose either the CPU or memory tabs.
- Click the top of the CPU or memory column to order processes according to the resources they are using.
- Play the video that was playing when you noticed the problem.
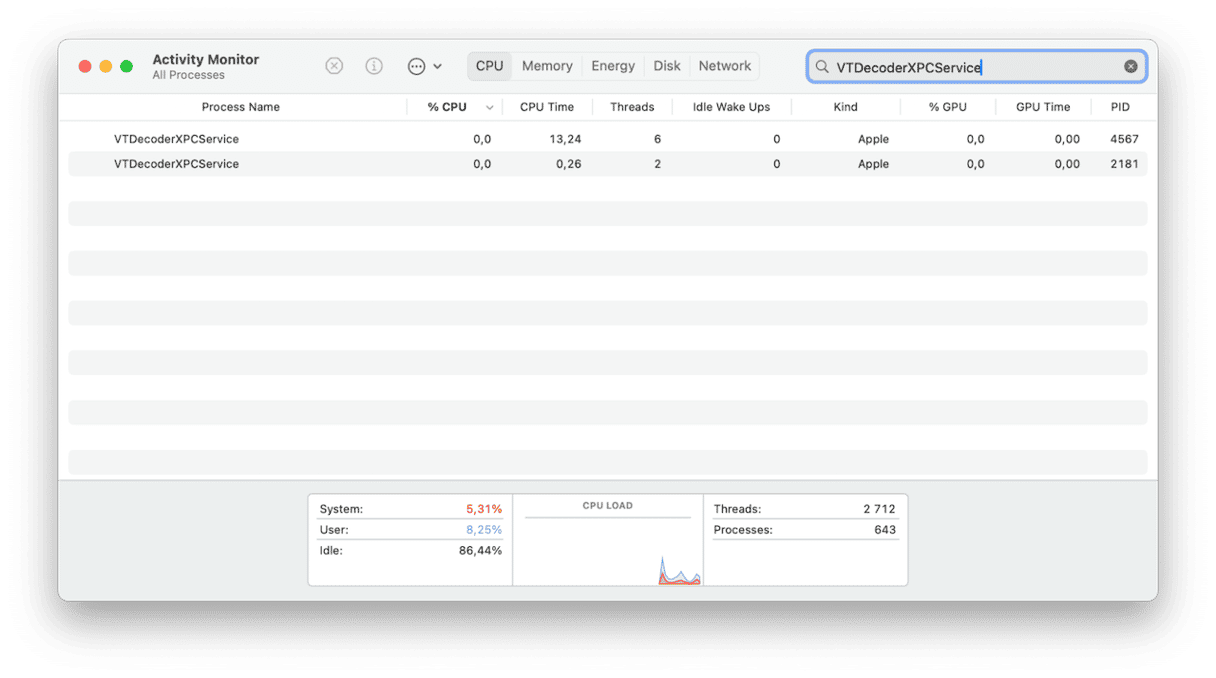
- If you notice VTDecoderXPCService using nearly all your Mac’s CPU cycles or several GB of RAM, you know it is causing the problem.
Once you’ve identified that VTDecoderXPCService is the problem, you can select it in Activity Monitor and click the ‘x’ in the toolbar to quit it. Then, quit Activity Monitor.
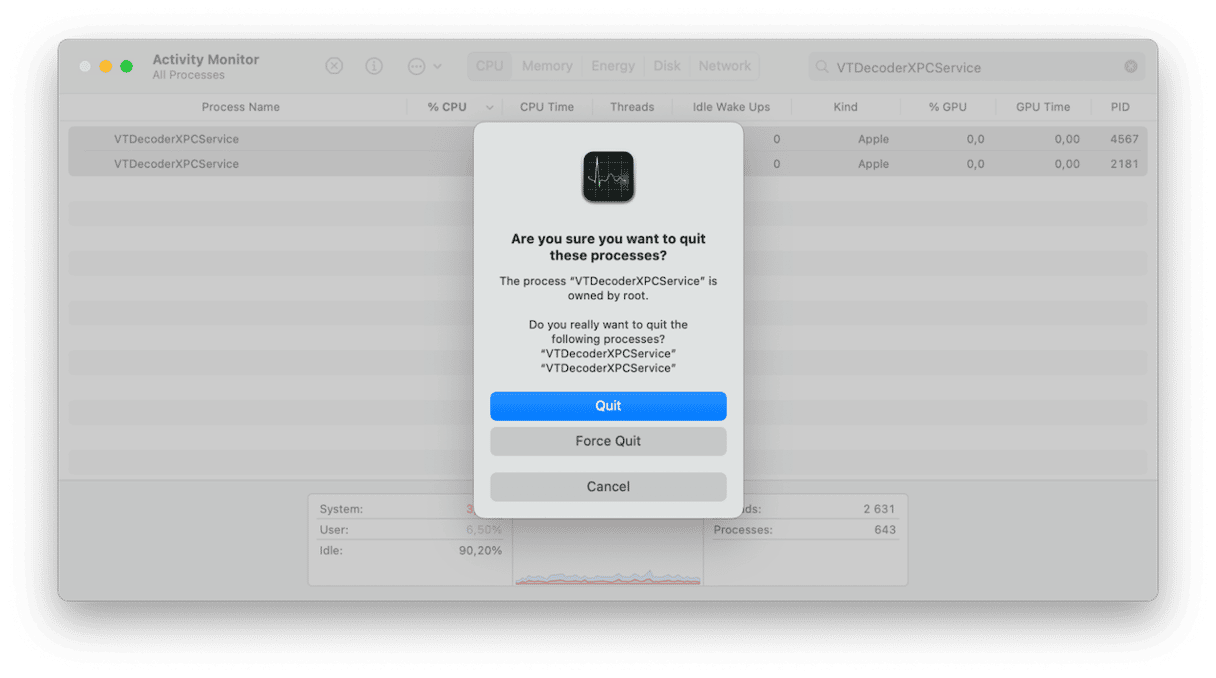
VTDecoderXPCService will then restart when it’s needed and you can carry on using your Mac as normal. That may be all you need to do. However, if the problem occurs again, you’ll need to take further action.
How to fix VTDecoderXPCService high CPU
If quitting VTDecoderXPCService did not help, there’s a lot else you can do.
1. Update macOS
It’s possible that the reason VTDecoderXPCService has high memory and CPU usage is a bug in the version of macOS installed on your Mac. That bug may cause a conflict with apps that are using the service. So, the next step is to check for an update.
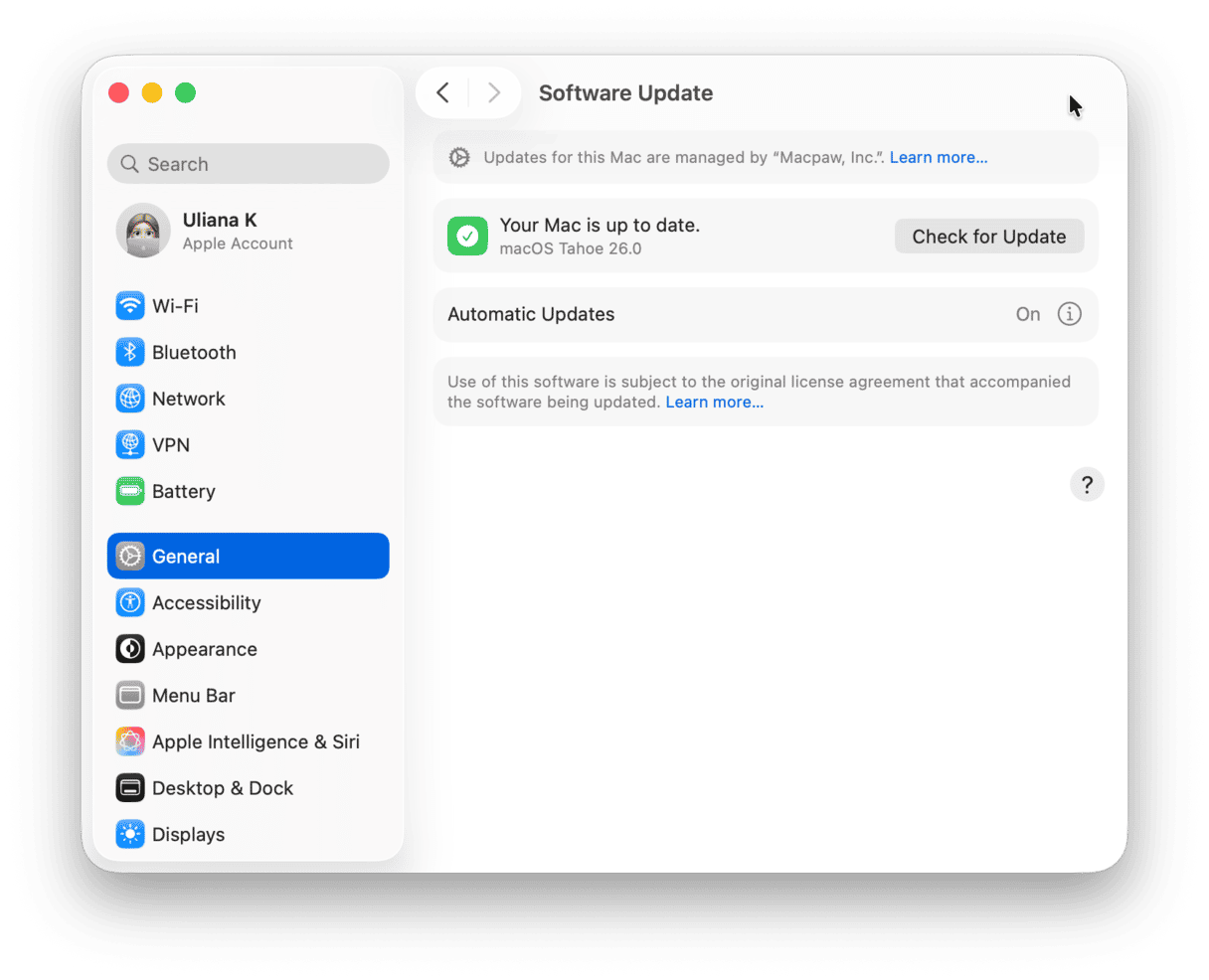
- Click the Apple menu and choose System Settings.
- Go to General > Software Update.
- Wait for it to check for updates.
- If there is one available, follow the steps on the screen to install it.
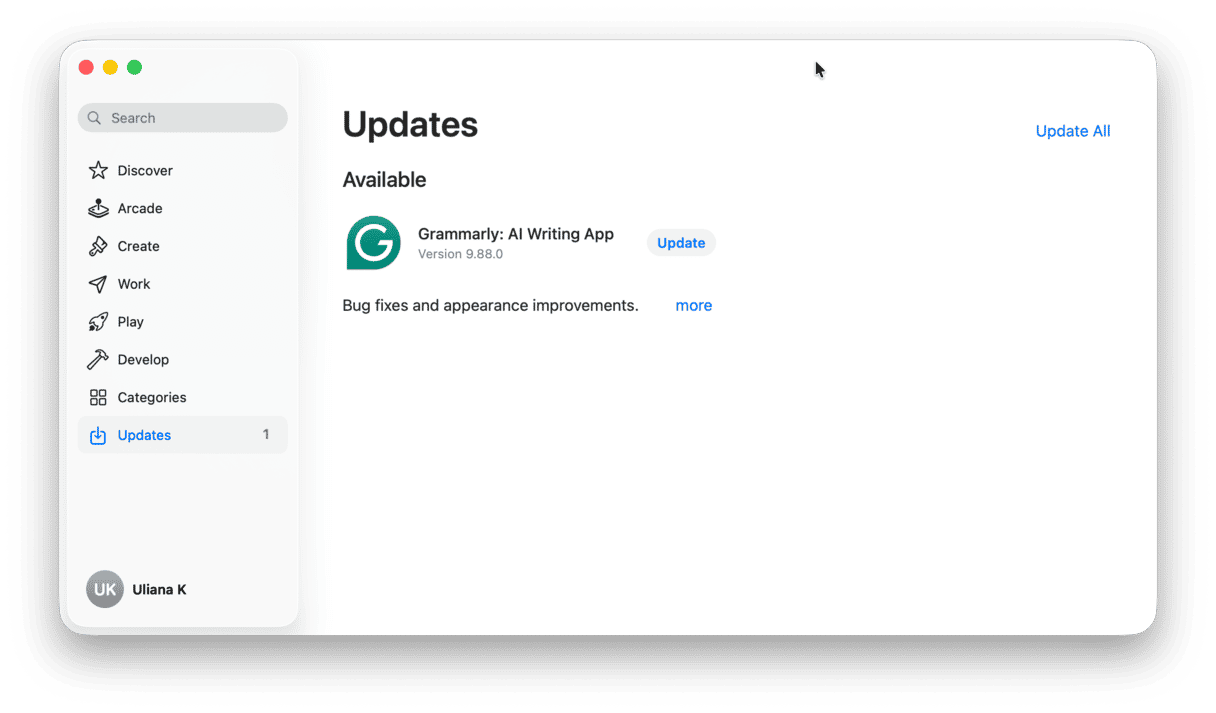
2. Update applications
If you notice that VTDecoderXPCService is hogging resources when you work with or watch a video in one specific app, check for updates to that app. If you downloaded the app from the App Store, you should launch the App Store app and go to the Updates section. If you downloaded the app from the developer’s website, you can either check the website or open the app, click the app name menu, and choose Check for Updates.
3. Clear browser cache
If the problem occurs when you watch videos in a web browser, it could be that the browser cache has grown very large and is causing problems for the browser. Emptying cache, especially in Chrome, can solve lots of problems. Here’s how to empty cache in Safari, Chrome, and Firefox.
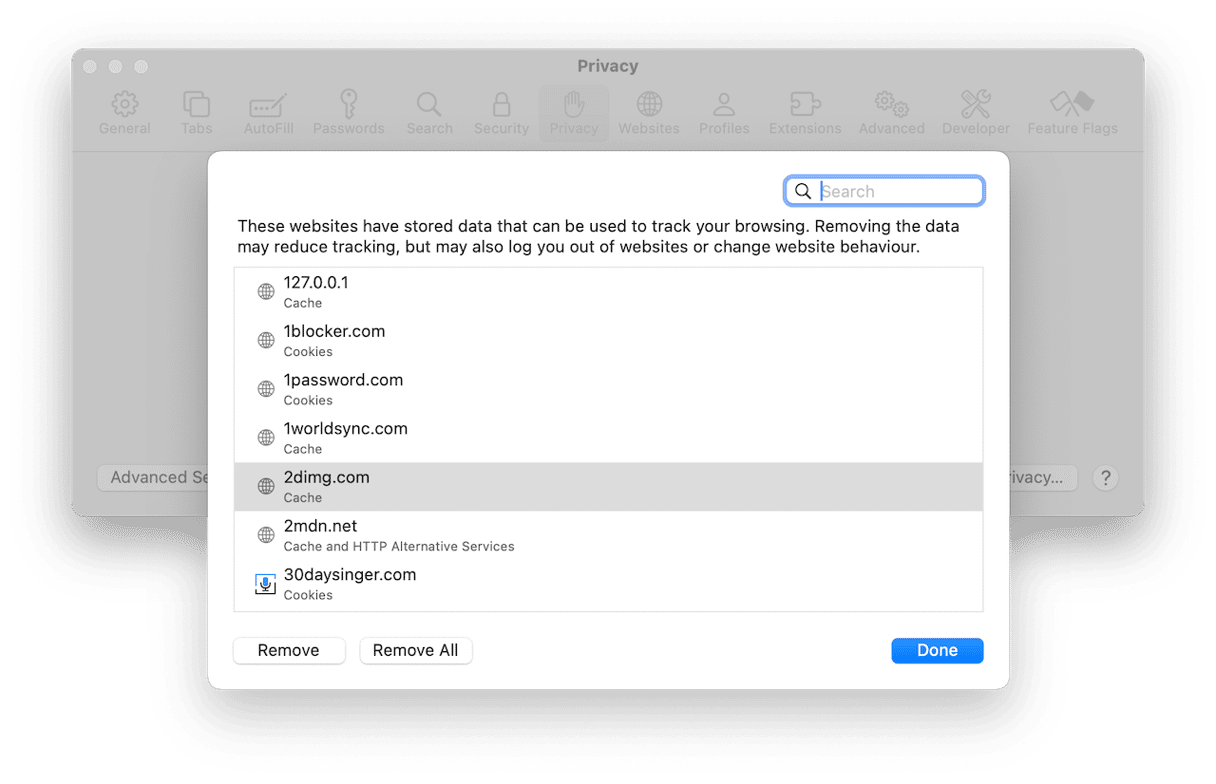
Safari
- Click the Safari menu and choose Settings.
- Choose Privacy, then click Website Data.
- Wait for the data to load, then either select a website and choose Remove or click Remove All to delete website data for all websites you’ve ever visited.
Chrome
- Click the three dots to the right of the address bar and choose Settings.
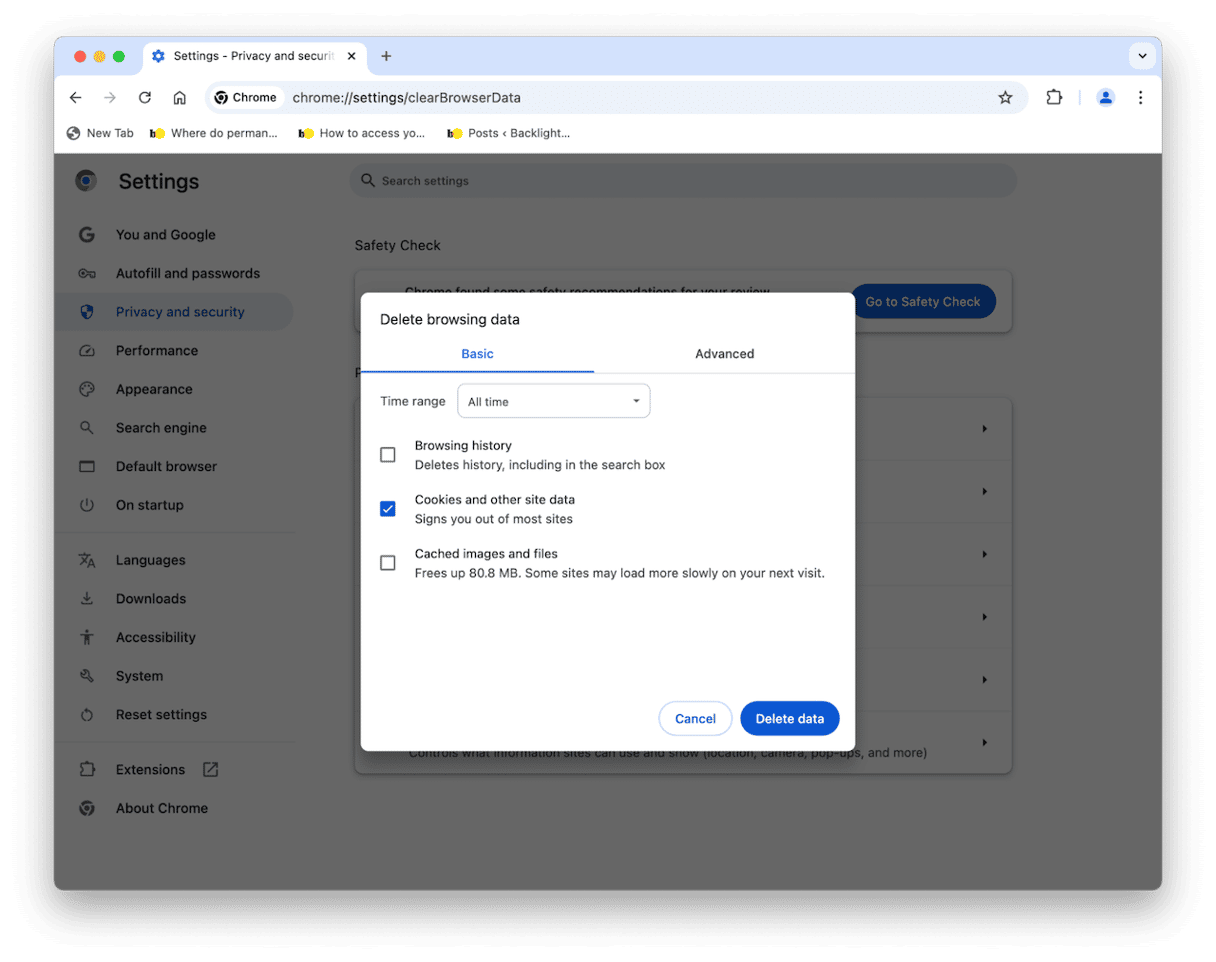
- Go to Privacy and security and then click Delete Browsing Data.
- Choose Cached Images and Files and click Delete Data.
Firefox
- Click the three horizontal lines next to the address bar.
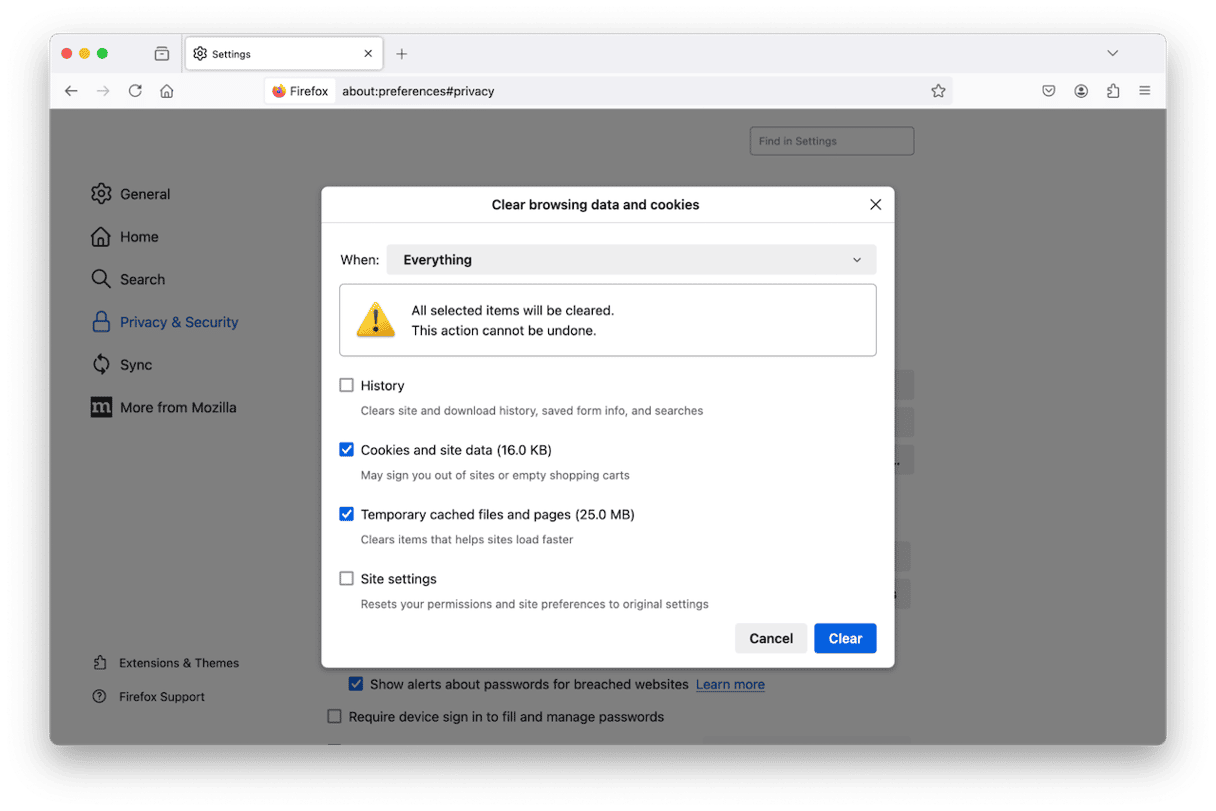
- Choose Settings > Privacy & Security.
- Scroll down to Cookies and Site Data.
- Click Clear Data to delete all cache and cookies, or Manage Data to choose what to delete.
Check for malware
If you can’t work out any other reason for VTDecoderXPCService using lots of memory and CPU cycles, it could be that your Mac is infected with malware. One of the effects of malware is that it interferes with other processes on your Mac, causing them to hang or have trouble running properly. To check whether there is malware on your Mac, you need a specialist tool.
We recommend CleanMyMac. It scans your Mac looking for adware, browser hijackers, crypto currency miners and other forms of malware. You can set it up to run a deep scan, a quick scan, or a balance of the two. And you can configure it to run only when you manually invoke it or in the background to keep your Mac safe from malware on an ongoing basis.
Here’s how to check your Mac for malware:
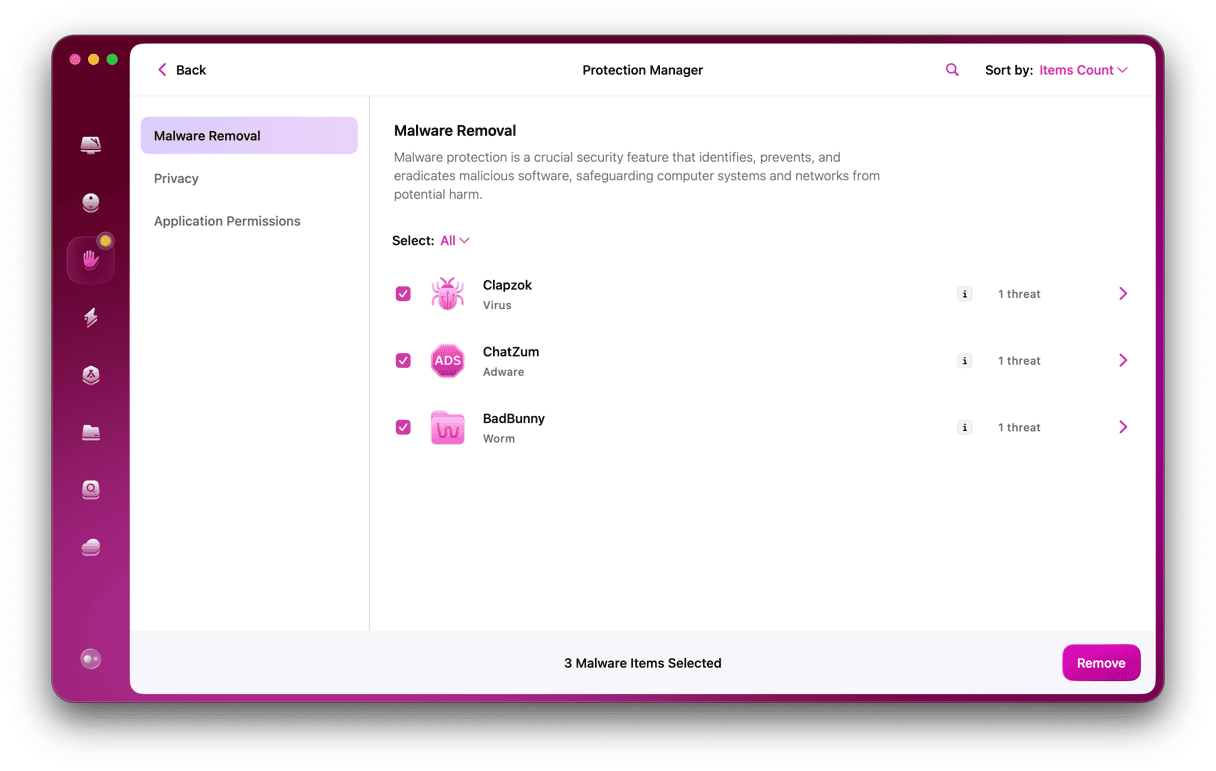
- Open CleanMyMac.
- Click Malware Removal > Scan.
- If malware has been detected, click Remove.
VTDecoderXPCService is a process in macOS that is called into action when you watch or work with video on your Mac. Among other things, it allows third-party applications to use your Mac’s GPU. Most of the time, you don’t need to think about it. But occasionally, things go wrong, and VTDecoderXPCService uses lots of memory or CPU cycles. If that happens on your Mac, follow the steps above to fix it.